HOWTO garmin GPS map
1. Download the DVD image from verycd.
http://www.verycd.com/topics/2721464/
2. Daemon tools Lite to mount the image file: .iso
3. Run CNNANT2009Update_ENU.msi from :\Windows\MSI\ and install the new maps onto hard drive
4. Connected GPS to your PC and turn on the power
5. In MapSource, get the Unit ID via Utilitis->Get Unit ID (write this down!)
6. Use Garmin Unlock Utility to generate a map unlock code for the new map software
7. in MapSource, unlock the new maps using the generated unlock code
8. Backup and then delete the gmapsupp.img file from the :\Garmin\ folder
9. Check the available space on
10. In MapSource, select the desired maps to copy to the GPS (make sure not to exceed available space) or open previously saved .GDB file
11. In MapSource, change the auto generated Map Set Name to a more descriptive name of the map set
12. In MapSource, transfer maps to device
Tuesday, December 30, 2008
Saturday, November 22, 2008
USA VISA (Vancouver)
Share 1
加拿大居民美国签证全攻略(温哥华,08年)
办理美国签证较为容易,只要有工作,加拿大的永久居民一般都能顺利地申请到美国十年期的签证。
步骤一
登记签证时间,至少提前两周安排时间。登陆此网站 http://www.nvars.com/
网上登记预约时间,预约费用为8.75加元。用信用卡登记比较方便。如果想电话咨询或预约,可以打1-900-451-2778,每分钟1.89元加币。
注意:Dependents number 如果是一家人,而不是一个人去签,注意正确填写这项的数量,否则门卫可能会拒绝你。比如你一家三口人,你是主申请人,你的太太和子女就是附属申请人,那就填2就可以了。
在网上注册后,可直接打印预约信,上面有你预约的时间、地点、你的一些预约资料。这张纸必须当天携带,如果你没有打印,也会在一周后收到一份完整的申请资料。
步骤二
在线填写DS-160. New form.
Link For 160
在线填写DS-156 evisaforms.state.gov
注意仔细填写每个问题,然后再按continue。如果填错也没关系,那个在线156的表格,continue后发现填错了就把窗口关掉,重新再填好,再 continue好了。那些信息不会存到数据库,都在条形码里面了。所以,填写到你觉得对了才打印。如果你打印出来才发现错了也没关系,在签证处2楼你也可以向保安说明需要,重新用手填写(当然最好是网上填写,这样会自动生成一个条形码,方便签证速度)。在说明中需要DS-156两份,实际情况他们只需要一份。
拍照,需要拍摄美国签证的专用照片,基本上每家照像馆都行。只需向摄影师说明就行。
DS-157表,男性都需要填写,手写就可以。
美国签证(B1,B2)关键是向签证官说明你没有意向在美国长期逗留,所以你必须准备能证明你在加拿大长期居住的证据。
1. 如果你是self-employed ,别忘了你的名片。
2. 如果是被雇用,准备好雇用信(下附雇主信的参考写法)。你的pay slips (就是公司给你支票的下面部分)。
3. 如果是学生,要有学校出具的证明信(不是学生证)和你的学费收据。
除此以外,枫叶卡,上月的银行对帐单,你的房子租约,汽车相关文件,和其他财产的相关资料。
别忘带上你的护照。
如果是家庭,带上能证明和主申请人关系的文件,比如IMM-1000。
当然还有每个人131美元的签证费payment。该签证费是要到指定的丰业银行(Scotia Bank),可以用现金或者信用卡支付。去银行交款之前一定要自己打印一式三联的交款单。交款单在网上下载,第一页。
签证通过后,使馆会将护照寄回给你,这里有两种方式你可以选择,一是带上你的信用卡,填写信用卡资料,以便使馆扣取邮寄护照的资费。二是自己到邮局买好已付资(prepaid)的快信信封,并填好你的地址,交给使馆。大约一周的时间就可以收到护照。
步骤三
准备好材料,预约好时间后(当前有效的预约时间可以在www.nvars.com/use/查到,如果想提前预约时间,没有其他办法,只能每天网上查查有没有人取消预约的,有的话就赶快插上去),那就讲讲签证。
温哥华的签证处地址:United States Consulate General
1075 West Pender Street, Vancouver, BC.
在大楼的侧面。
签证前注意不要带任何电子产品(手机,计算器,laptop.mp3…..)如果带了,不能让你进就麻烦了。单身男士都不可以带包,女士可以带个小包,包里东西尽量少,否则检查时间会很长。不要提前买食物和饮料,门卫可能会要求你处理掉他们。
提前10-20分种到就可以,整个签证时间大约为1-2.5hours。
开始会在门口排队,按顺序进入侧门。在侧门需要第一次检查,准备好护照,移民卡,预约信。按门卫要求,除去外套,等等。别太着急通过安检门。
按部就班的到2楼,按顺序坐好,门卫会提醒你去交材料和费用凭证。这时候你会领到一个号码。
按这个号码的提示,坐电梯到20楼,再做一个检查,就能面对签证官了。
只要材料准备好,不用担心。向签证官证明你当前在加拿大的生活稳定,有长期的计划和没有在美国长期逗留的企图。
一切OK后,就可以在家等着收护照了。
就大家关心的问题,再强调以下注意事项:
1、 预约方式最好使用网上预约,通过电话不够直观,而且至少需要10元以上加币才能完成预约。
2、 填写申请最好不要有空项,赴美目的一栏通常为“tour”,地点“Seattle”,时间“one day”,告诉签证官你不在美国住宿,当天往返。也可以写去拉斯维加斯,时间就写多几天。
3、 有时签证官会问到你到美国的具体目的,最好准备一个充分的理由。
4、 不要提在美国有亲戚、朋友,签证官怕你滞美不归。
5、 按预约时间准时到,可以提前一点,但不要迟到。
6、 开车的朋友更要提前,因为那里不太好停车,也可以坐公交车去。乘车路线: 98B-line 或 sky train 到Burrard Station 即可。
7、 获得签证的, 签证官会留下你的护照,同时给你一张取护照的收据。
8、 被拒签的,当时在护照上盖上拒签章, 并还给你。
9、 签证时可以带翻译员。一家人申请时,孩子满了14岁,也要一起去。
10、 如果中国护照快过期(少于半年),要去中国大使馆办续期后再去签。
11、 对于新移民最好住满1年,有工作的,工作时间最好满半年。
附:雇主信的参考信写法:
To Whom It May Concern:
Please accept this letter as confirmation of the employment of xxx at yyyy.
xxx’s position is Engineer in our company. xxx began her employment from mm-yy with salary $$$$$.
If you have any further questions, please call at (604) ***-****.
Sincerely yours,
附一些问题的问答:
问:DS156中,national indentification number 填写什么? 是中国的身份证号码吗?
另外 ,DS157 中 Full name in Native Alphabet 写什么? 是中文名字吗?
答:1、是中国的身份证号码
2、是填中文名字(用中文填)
问:DS- 157表第八项“Full Name and Address of Contact Person or Organization inthe United States (Include Telephone Number)”如果没有是不是可以不填?
答:填N/A(或None)。
问:DS157上的9栏,去过哪些国家?是不是把签证页上有的写上就OK了?
答:是,个人认为你去的发达国家越多越可以证明你没有移民倾向。
问:Confirmation letter有好多页,只须打印首页,还是全部打印?我们共三人,要打印三份以不同人名申请的DS-156表格吗?
答:预约的确认信,打印第一页有预约内容的就ok了。三人的都要打印,每份3页。
Share 2
【分享】我的温哥华美国签证过程
很感谢这里的分享,让我自己在办理美国签证的时候也非常顺利.所以在此也想和大家说说我的经历.希望对以后的兄弟姐妹有所帮助.
刷新了无数次卡尔加里,几个月下来还是没有available,索性就定了温哥华,正好旅游一下.温哥华的预约真的是多的很,而且据我发现,一般在温哥华时间晚上12点以后,都会有新的预约出现.比如说,现在在白天的时候网站上只会看到1月份的预约,但是过了12点,就会出现11月底和12月的预约,大概是很多cancel的.这些预约会很快没有,到了白天就看不到了.
准备资料也是根据网上大家说的那样.
我老公填了DS-156和157,我只需要156(157只需要男士填).157我是打印的,因为这个文件不能保存,只能直接打印.DS-156可以保存下来,然后去别处打印也可以.两个材料上不会填的或者不要填的都可以空着.
因为我目前没有工作,就只让老公准备了employment letter.其他材料比如银行的monthly statement,还有税单,payment slip我都按要求准备齐全.
然后跑到scotia bank交了每人100美金的申请费,银行stamp之后还给我两张单子,他收去一张.
没有符合尺寸的照片,美国人真讨厌,居然要求那么奇怪的2*2,只好和lg重新照了.(在温哥华美领馆我也没发现有照相的机器).
我预约的是7点半,是最早的一批,大概7点15到,已经有几个人在排队了. 门口按照半小时一队分开排列着.大概到了40分,有个女的出来告诉大家要有scotia bank的付费单,没有的话要先去付掉再进去.就有一两个人大概没有付,拿了单子出去付钱了.然后那个女的又给每人一张canada post的快递单,要求大家填好,因为上面要有信用卡信息,又有些人没带.其实没有关系,或者可以打电话回去问家人(过了安检有打公用电话的地方),或者当场用别人的,只是用于快递费而已.
先是在门口安检,那个安检的黑人很不友好,lg稍微慢了一点,他就跟我说why he is so slow.上了狭窄的楼梯,门口有个黑人让大家按照纸上要求的准备好资料,然后进门排队递交材料.一个女的比较nice的签证官会收掉护照和 ds156,157表格以及雇主信,看一下移民卡填上号码在156表格上还给我们,给了一张号,让我们坐下等着.我们拿到了4号.
乘电梯上了20楼,继续安检,完毕后,进入签证厅.走廊很狭窄,一排椅子,对着签证窗口.
先有个窗口开了,是按指纹的.按好指纹继续等待.很快又开了一个窗口,叫了1号.那个1号申请的人好像是印度或者南美吧.跑到那个窗口很多时间都没好.接着第二个窗口开了,就是我坐着面对的那个,是个胖胖的男签证官.叫了2号.整个过程估计就2分钟吧,问了那个女的是干嘛的,呆了几年回答说是先来念书的, 现在工作了.签证官问有没有拿到diploma,她说是的.然后问什么时候结婚的,老公是否是公民和什么工作.就这么结束了.我心里就在想,唉我们是4 号,估计轮不到这个窗口了.
结果surprise了,签证官叫了4号.
签证官:are u husband and wife?
us:yes
vo:how long have u been here?
us:1year
然后签证管看了lg的雇主信,问是不是新的工作.lg一下没听懂没回答.
他又问我在干嘛?我说我刚辞了part-time的job,现在在uc上课.他问是什么课.还有国内是不是有学历.
接着又问我们以前在国内干什么的.还有老公的学历.老公说是检验师,他说在这里有没有拿到证书,我们回答说没有,很难,而且英语不好.vo很nice的说 takes time.他又接着问lg这份工作多长时间了,lg说1年.问我们去美国干嘛,我们当然回答说是去shopping拉.
问完这些,他就说快递单填了没有,说visa approved了.最长一周的时间寄到.
整个时间也就5分钟.除了雇主信什么都没看.
等我们结束了,我看那个1号还没好.
出了领管楼,才8点45,很快哦,1个小时.所以我觉得情愿预约的早一点,早点去早点出来.到后面等的时间就会越来越长了.
希望我上面的分享有帮助哦.
Share 3
前几天搞到美国的十年签证顺便去离温哥华最近的美国小城转了一下,买了一点东西,有部分程序更改了,补充一下。
Share 4
我妈是到加拿大探亲的, 来了有一个月, 明年三月份回国, 春节前后准备带她到LAS VEGAS玩一玩. 我妈没有亲属在美国, 不懂英文. 我和老公移民加拿大四年, 都有稳定工作, 也有美国签证, 去美国玩过一次.
签证经过:
8:30到了领事馆: 预约的时间是早9点, 我和妈妈提前半小时到, 使馆前已经排起了长龙, 分为8:00, 8:30, 9:00三个队.
9:10进入使馆: 经过安检(非常严格, 不准带任何电子设备包括手机, 也不能带大包), 到二楼排队交申请费100美元, 领取一个号码后到大厅里等待.
10:20上20楼: 当电子屏幕上显示出持有的号码时出大厅坐电梯到20楼准备见签证官, 又经过一次安检, 然后进入一个长形的走廊, 到1号窗口前按指纹, 之后又是等待叫号.
10:50分左右终于见到了签证官. 我解释妈妈不懂英文所以我是翻译. 签证官是个50岁左右的老头儿, 很和蔼, 还开玩笑说那我妈有我这个女儿很幸运了. 看我们写的是到VEGAS去旅游, 就问我明年是中国的什么年. 我说是狗年(YEAR OF DOG), 他又问是不是很LUCKY的年, 我说不算吧. 之后才问我和老公的一些情况, 比如来加拿大多久了, 做什么工作的, 我一边回答他一变快速的看了看我和老公的材料, 他的目光只是在我的雇主信上多停留了几秒, 然后就说明天下午三点来拿签证吧. 我妈的材料他从头到尾一个也没看, 也没问和我妈有关的任何问题. 前后大约10分钟.
11:00面试结束. 感觉好象太轻松了, 都有点不太相信. 我们前后10个申请只有1个被拒签了(两个签证官), 是一家三口从大陆来的移民, 所以感觉通过率还是很高的, 是圣诞节前的缘故吗? 不太清楚, 但移民官的心情看上去都不错.
今天下午3点拿到了签证, 一年多次往返.
我准备的材料有:
APPLICANT (MY MOM):
1.DS-156 with photo attached
2.Valid Passport
3.Notarized Certificate of Real Estate Property
4.Bank Statement of Savings
5.Retirement Certificate
6.Itinerary to Las Vegas
7.Airline ticket returning to China
SPONSORS (ME & MY HUSBAND):
1.Valid Passports with US Visas
2.Canadian Permanent Residence Cards
3.Letters of Employment
4.Pay Slips and tax documents
5.Bank Statements
6.Rental Agreement
7.Notarized Birth Certificate (proof of relationship with the applicant)
1.这个网上预约面试时间,交钱,要打印出来预约信,使馆不寄了
2.网上添156表(必须网上填写和打印,手写的不行),这个错了可以重填重新打印,男的要添157表,这个表设计不合理,我是部分用手写的。
3.相片自己照和打印的,按照要求来就好了,比照相馆肯定便宜了
4.使馆现在不收现金了,到了门口警卫会给表格,每个人一份,去附近的银行(表格上有地图)交钱盖章
5.首次等待叫号的房子味道很难闻,恨不得带个防毒面具去:)
6.签证官基本都是年轻人,感觉都很nice, 我英语不好,经常答非所问,也没要任何其他证明就给了签证,应该是和一家人有关,我特别提到了圣诞节去夏威夷,感觉绝对是个好理由
7.护照现首先推荐邮寄,这个需要带一张信用卡,填写邮寄的地址时候需要(邮寄肯定你出钱了)。当天我看有人没带信用卡,估计也可以第二天去取,不过我先出来了,不能确认。邮寄的护照我一个星期后收到
收到护照后就顺便去美国转一圈,去的时候是星期五觉得过关时间应该短,结果排队还是花了将近2个小时,回来花了差不多1个半小时,买了100刀的东西外加一箱汽油,是感觉美国东西便宜,税也少。不过排队时间实在太长,实在没有耐心再次去。首次进入美国要去一个office简单问一下,然后每个人再交6刀,半年之内的再次进入美国好像不用再交了,半年之后依然要再次询问加交钱。
http://www.consular.canada.usembassy.gov/vancouver.asp
Share 1
加拿大居民美国签证全攻略(温哥华,08年)
办理美国签证较为容易,只要有工作,加拿大的永久居民一般都能顺利地申请到美国十年期的签证。
步骤一
登记签证时间,至少提前两周安排时间。登陆此网站 http://www.nvars.com/
网上登记预约时间,预约费用为8.75加元。用信用卡登记比较方便。如果想电话咨询或预约,可以打1-900-451-2778,每分钟1.89元加币。
注意:Dependents number 如果是一家人,而不是一个人去签,注意正确填写这项的数量,否则门卫可能会拒绝你。比如你一家三口人,你是主申请人,你的太太和子女就是附属申请人,那就填2就可以了。
在网上注册后,可直接打印预约信,上面有你预约的时间、地点、你的一些预约资料。这张纸必须当天携带,如果你没有打印,也会在一周后收到一份完整的申请资料。
步骤二
在线填写DS-160. New form.
Link For 160
在线填写DS-156 evisaforms.state.gov
注意仔细填写每个问题,然后再按continue。如果填错也没关系,那个在线156的表格,continue后发现填错了就把窗口关掉,重新再填好,再 continue好了。那些信息不会存到数据库,都在条形码里面了。所以,填写到你觉得对了才打印。如果你打印出来才发现错了也没关系,在签证处2楼你也可以向保安说明需要,重新用手填写(当然最好是网上填写,这样会自动生成一个条形码,方便签证速度)。在说明中需要DS-156两份,实际情况他们只需要一份。
拍照,需要拍摄美国签证的专用照片,基本上每家照像馆都行。只需向摄影师说明就行。
DS-157表,男性都需要填写,手写就可以。
美国签证(B1,B2)关键是向签证官说明你没有意向在美国长期逗留,所以你必须准备能证明你在加拿大长期居住的证据。
1. 如果你是self-employed ,别忘了你的名片。
2. 如果是被雇用,准备好雇用信(下附雇主信的参考写法)。你的pay slips (就是公司给你支票的下面部分)。
3. 如果是学生,要有学校出具的证明信(不是学生证)和你的学费收据。
除此以外,枫叶卡,上月的银行对帐单,你的房子租约,汽车相关文件,和其他财产的相关资料。
别忘带上你的护照。
如果是家庭,带上能证明和主申请人关系的文件,比如IMM-1000。
当然还有每个人131美元的签证费payment。该签证费是要到指定的丰业银行(Scotia Bank),可以用现金或者信用卡支付。去银行交款之前一定要自己打印一式三联的交款单。交款单在网上下载,第一页。
签证通过后,使馆会将护照寄回给你,这里有两种方式你可以选择,一是带上你的信用卡,填写信用卡资料,以便使馆扣取邮寄护照的资费。二是自己到邮局买好已付资(prepaid)的快信信封,并填好你的地址,交给使馆。大约一周的时间就可以收到护照。
步骤三
准备好材料,预约好时间后(当前有效的预约时间可以在www.nvars.com/use/查到,如果想提前预约时间,没有其他办法,只能每天网上查查有没有人取消预约的,有的话就赶快插上去),那就讲讲签证。
温哥华的签证处地址:United States Consulate General
1075 West Pender Street, Vancouver, BC.
在大楼的侧面。
签证前注意不要带任何电子产品(手机,计算器,laptop.mp3…..)如果带了,不能让你进就麻烦了。单身男士都不可以带包,女士可以带个小包,包里东西尽量少,否则检查时间会很长。不要提前买食物和饮料,门卫可能会要求你处理掉他们。
提前10-20分种到就可以,整个签证时间大约为1-2.5hours。
开始会在门口排队,按顺序进入侧门。在侧门需要第一次检查,准备好护照,移民卡,预约信。按门卫要求,除去外套,等等。别太着急通过安检门。
按部就班的到2楼,按顺序坐好,门卫会提醒你去交材料和费用凭证。这时候你会领到一个号码。
按这个号码的提示,坐电梯到20楼,再做一个检查,就能面对签证官了。
只要材料准备好,不用担心。向签证官证明你当前在加拿大的生活稳定,有长期的计划和没有在美国长期逗留的企图。
一切OK后,就可以在家等着收护照了。
就大家关心的问题,再强调以下注意事项:
1、 预约方式最好使用网上预约,通过电话不够直观,而且至少需要10元以上加币才能完成预约。
2、 填写申请最好不要有空项,赴美目的一栏通常为“tour”,地点“Seattle”,时间“one day”,告诉签证官你不在美国住宿,当天往返。也可以写去拉斯维加斯,时间就写多几天。
3、 有时签证官会问到你到美国的具体目的,最好准备一个充分的理由。
4、 不要提在美国有亲戚、朋友,签证官怕你滞美不归。
5、 按预约时间准时到,可以提前一点,但不要迟到。
6、 开车的朋友更要提前,因为那里不太好停车,也可以坐公交车去。乘车路线: 98B-line 或 sky train 到Burrard Station 即可。
7、 获得签证的, 签证官会留下你的护照,同时给你一张取护照的收据。
8、 被拒签的,当时在护照上盖上拒签章, 并还给你。
9、 签证时可以带翻译员。一家人申请时,孩子满了14岁,也要一起去。
10、 如果中国护照快过期(少于半年),要去中国大使馆办续期后再去签。
11、 对于新移民最好住满1年,有工作的,工作时间最好满半年。
附:雇主信的参考信写法:
To Whom It May Concern:
Please accept this letter as confirmation of the employment of xxx at yyyy.
xxx’s position is Engineer in our company. xxx began her employment from mm-yy with salary $$$$$.
If you have any further questions, please call at (604) ***-****.
Sincerely yours,
附一些问题的问答:
问:DS156中,national indentification number 填写什么? 是中国的身份证号码吗?
另外 ,DS157 中 Full name in Native Alphabet 写什么? 是中文名字吗?
答:1、是中国的身份证号码
2、是填中文名字(用中文填)
问:DS- 157表第八项“Full Name and Address of Contact Person or Organization inthe United States (Include Telephone Number)”如果没有是不是可以不填?
答:填N/A(或None)。
问:DS157上的9栏,去过哪些国家?是不是把签证页上有的写上就OK了?
答:是,个人认为你去的发达国家越多越可以证明你没有移民倾向。
问:Confirmation letter有好多页,只须打印首页,还是全部打印?我们共三人,要打印三份以不同人名申请的DS-156表格吗?
答:预约的确认信,打印第一页有预约内容的就ok了。三人的都要打印,每份3页。
Share 2
【分享】我的温哥华美国签证过程
很感谢这里的分享,让我自己在办理美国签证的时候也非常顺利.所以在此也想和大家说说我的经历.希望对以后的兄弟姐妹有所帮助.
刷新了无数次卡尔加里,几个月下来还是没有available,索性就定了温哥华,正好旅游一下.温哥华的预约真的是多的很,而且据我发现,一般在温哥华时间晚上12点以后,都会有新的预约出现.比如说,现在在白天的时候网站上只会看到1月份的预约,但是过了12点,就会出现11月底和12月的预约,大概是很多cancel的.这些预约会很快没有,到了白天就看不到了.
准备资料也是根据网上大家说的那样.
我老公填了DS-156和157,我只需要156(157只需要男士填).157我是打印的,因为这个文件不能保存,只能直接打印.DS-156可以保存下来,然后去别处打印也可以.两个材料上不会填的或者不要填的都可以空着.
因为我目前没有工作,就只让老公准备了employment letter.其他材料比如银行的monthly statement,还有税单,payment slip我都按要求准备齐全.
然后跑到scotia bank交了每人100美金的申请费,银行stamp之后还给我两张单子,他收去一张.
没有符合尺寸的照片,美国人真讨厌,居然要求那么奇怪的2*2,只好和lg重新照了.(在温哥华美领馆我也没发现有照相的机器).
我预约的是7点半,是最早的一批,大概7点15到,已经有几个人在排队了. 门口按照半小时一队分开排列着.大概到了40分,有个女的出来告诉大家要有scotia bank的付费单,没有的话要先去付掉再进去.就有一两个人大概没有付,拿了单子出去付钱了.然后那个女的又给每人一张canada post的快递单,要求大家填好,因为上面要有信用卡信息,又有些人没带.其实没有关系,或者可以打电话回去问家人(过了安检有打公用电话的地方),或者当场用别人的,只是用于快递费而已.
先是在门口安检,那个安检的黑人很不友好,lg稍微慢了一点,他就跟我说why he is so slow.上了狭窄的楼梯,门口有个黑人让大家按照纸上要求的准备好资料,然后进门排队递交材料.一个女的比较nice的签证官会收掉护照和 ds156,157表格以及雇主信,看一下移民卡填上号码在156表格上还给我们,给了一张号,让我们坐下等着.我们拿到了4号.
乘电梯上了20楼,继续安检,完毕后,进入签证厅.走廊很狭窄,一排椅子,对着签证窗口.
先有个窗口开了,是按指纹的.按好指纹继续等待.很快又开了一个窗口,叫了1号.那个1号申请的人好像是印度或者南美吧.跑到那个窗口很多时间都没好.接着第二个窗口开了,就是我坐着面对的那个,是个胖胖的男签证官.叫了2号.整个过程估计就2分钟吧,问了那个女的是干嘛的,呆了几年回答说是先来念书的, 现在工作了.签证官问有没有拿到diploma,她说是的.然后问什么时候结婚的,老公是否是公民和什么工作.就这么结束了.我心里就在想,唉我们是4 号,估计轮不到这个窗口了.
结果surprise了,签证官叫了4号.
签证官:are u husband and wife?
us:yes
vo:how long have u been here?
us:1year
然后签证管看了lg的雇主信,问是不是新的工作.lg一下没听懂没回答.
他又问我在干嘛?我说我刚辞了part-time的job,现在在uc上课.他问是什么课.还有国内是不是有学历.
接着又问我们以前在国内干什么的.还有老公的学历.老公说是检验师,他说在这里有没有拿到证书,我们回答说没有,很难,而且英语不好.vo很nice的说 takes time.他又接着问lg这份工作多长时间了,lg说1年.问我们去美国干嘛,我们当然回答说是去shopping拉.
问完这些,他就说快递单填了没有,说visa approved了.最长一周的时间寄到.
整个时间也就5分钟.除了雇主信什么都没看.
等我们结束了,我看那个1号还没好.
出了领管楼,才8点45,很快哦,1个小时.所以我觉得情愿预约的早一点,早点去早点出来.到后面等的时间就会越来越长了.
希望我上面的分享有帮助哦.
Share 3
前几天搞到美国的十年签证顺便去离温哥华最近的美国小城转了一下,买了一点东西,有部分程序更改了,补充一下。
Share 4
我妈是到加拿大探亲的, 来了有一个月, 明年三月份回国, 春节前后准备带她到LAS VEGAS玩一玩. 我妈没有亲属在美国, 不懂英文. 我和老公移民加拿大四年, 都有稳定工作, 也有美国签证, 去美国玩过一次.
签证经过:
8:30到了领事馆: 预约的时间是早9点, 我和妈妈提前半小时到, 使馆前已经排起了长龙, 分为8:00, 8:30, 9:00三个队.
9:10进入使馆: 经过安检(非常严格, 不准带任何电子设备包括手机, 也不能带大包), 到二楼排队交申请费100美元, 领取一个号码后到大厅里等待.
10:20上20楼: 当电子屏幕上显示出持有的号码时出大厅坐电梯到20楼准备见签证官, 又经过一次安检, 然后进入一个长形的走廊, 到1号窗口前按指纹, 之后又是等待叫号.
10:50分左右终于见到了签证官. 我解释妈妈不懂英文所以我是翻译. 签证官是个50岁左右的老头儿, 很和蔼, 还开玩笑说那我妈有我这个女儿很幸运了. 看我们写的是到VEGAS去旅游, 就问我明年是中国的什么年. 我说是狗年(YEAR OF DOG), 他又问是不是很LUCKY的年, 我说不算吧. 之后才问我和老公的一些情况, 比如来加拿大多久了, 做什么工作的, 我一边回答他一变快速的看了看我和老公的材料, 他的目光只是在我的雇主信上多停留了几秒, 然后就说明天下午三点来拿签证吧. 我妈的材料他从头到尾一个也没看, 也没问和我妈有关的任何问题. 前后大约10分钟.
11:00面试结束. 感觉好象太轻松了, 都有点不太相信. 我们前后10个申请只有1个被拒签了(两个签证官), 是一家三口从大陆来的移民, 所以感觉通过率还是很高的, 是圣诞节前的缘故吗? 不太清楚, 但移民官的心情看上去都不错.
今天下午3点拿到了签证, 一年多次往返.
我准备的材料有:
APPLICANT (MY MOM):
1.DS-156 with photo attached
2.Valid Passport
3.Notarized Certificate of Real Estate Property
4.Bank Statement of Savings
5.Retirement Certificate
6.Itinerary to Las Vegas
7.Airline ticket returning to China
SPONSORS (ME & MY HUSBAND):
1.Valid Passports with US Visas
2.Canadian Permanent Residence Cards
3.Letters of Employment
4.Pay Slips and tax documents
5.Bank Statements
6.Rental Agreement
7.Notarized Birth Certificate (proof of relationship with the applicant)
1.这个网上预约面试时间,交钱,要打印出来预约信,使馆不寄了
2.网上添156表(必须网上填写和打印,手写的不行),这个错了可以重填重新打印,男的要添157表,这个表设计不合理,我是部分用手写的。
3.相片自己照和打印的,按照要求来就好了,比照相馆肯定便宜了
4.使馆现在不收现金了,到了门口警卫会给表格,每个人一份,去附近的银行(表格上有地图)交钱盖章
5.首次等待叫号的房子味道很难闻,恨不得带个防毒面具去:)
6.签证官基本都是年轻人,感觉都很nice, 我英语不好,经常答非所问,也没要任何其他证明就给了签证,应该是和一家人有关,我特别提到了圣诞节去夏威夷,感觉绝对是个好理由
7.护照现首先推荐邮寄,这个需要带一张信用卡,填写邮寄的地址时候需要(邮寄肯定你出钱了)。当天我看有人没带信用卡,估计也可以第二天去取,不过我先出来了,不能确认。邮寄的护照我一个星期后收到
收到护照后就顺便去美国转一圈,去的时候是星期五觉得过关时间应该短,结果排队还是花了将近2个小时,回来花了差不多1个半小时,买了100刀的东西外加一箱汽油,是感觉美国东西便宜,税也少。不过排队时间实在太长,实在没有耐心再次去。首次进入美国要去一个office简单问一下,然后每个人再交6刀,半年之内的再次进入美国好像不用再交了,半年之后依然要再次询问加交钱。
http://www.consular.canada.usembassy.gov/vancouver.asp
Friday, November 21, 2008
Howto Test Jumbo packets?
1, Generate Jumbo packet from SmartFlow (smartbit600)
Note: SmartFlow will count the frame bigger than 10004 byte (with CRC and VLAN) as lost frames.

2, HP procurve: after configure below command, HP can support up to 9220.
Link
#vlan 901 jumbo
#vlan 902 jumbo
3, FortiOS:
NP2 port does not support jumbor frames. So we can't override mtu value under NP2 ports
e1000 driver can support 16110 bytes.
tg3 driver can support 9000 bytes. (B32875 traced the details)
1, Generate Jumbo packet from SmartFlow (smartbit600)
Note: SmartFlow will count the frame bigger than 10004 byte (with CRC and VLAN) as lost frames.

2, HP procurve: after configure below command, HP can support up to 9220.
Link
#vlan 901 jumbo
#vlan 902 jumbo
3, FortiOS:
NP2 port does not support jumbor frames. So we can't override mtu value under NP2 ports
e1000 driver can support 16110 bytes.
tg3 driver can support 9000 bytes. (B32875 traced the details)
Sunday, November 2, 2008
Lab2
1.4 Configure R3 to poll R4 every 5 seconds.
R3:
interface Serial1/0.34 point-to-point
frame-relay interface-dlci 304
class FREEK
!m
ap-class frame-relay FREEK
frame-relay end-to-end keepalive mode request
frame-relay end-to-end keepalive timer send 5
1.6 PPP over Ethernet. Provide the security between AS100 and AS200's ethernet connection. R5 Dial R6.
R5:
username AS100 password 0 CISCO
!
interface Ethernet0/1
pppoe enable
pppoe-client dial-pool-number 1
!i
nterface Dialer1
mtu 1492
ip address 24.1.56.5 255.255.255.0
encapsulation ppp
dialer pool 1
dialer persistent
ppp authentication chap
ppp chap hostname AS200
R6:
username AS200 password 0 CISCO
!
vpdn enable
!v
pdn-group 1
accept-dialin
protocol pppoe
virtual-tempate 1
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/
pppoe enable
!i
nterface Virtual-Template1
ip address 24.1.56.6 255.255.255.0
ppp authentication chap
ppp chap hostname AS100
1.4 Configure R3 to poll R4 every 5 seconds.
R3:
interface Serial1/0.34 point-to-point
frame-relay interface-dlci 304
class FREEK
!m
ap-class frame-relay FREEK
frame-relay end-to-end keepalive mode request
frame-relay end-to-end keepalive timer send 5
1.6 PPP over Ethernet. Provide the security between AS100 and AS200's ethernet connection. R5 Dial R6.
R5:
username AS100 password 0 CISCO
!
interface Ethernet0/1
pppoe enable
pppoe-client dial-pool-number 1
!i
nterface Dialer1
mtu 1492
ip address 24.1.56.5 255.255.255.0
encapsulation ppp
dialer pool 1
dialer persistent
ppp authentication chap
ppp chap hostname AS200
R6:
username AS200 password 0 CISCO
!
vpdn enable
!v
pdn-group 1
accept-dialin
protocol pppoe
virtual-tempate 1
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/
pppoe enable
!i
nterface Virtual-Template1
ip address 24.1.56.6 255.255.255.0
ppp authentication chap
ppp chap hostname AS100
Monday, October 20, 2008
Howto admin HP 3500yl
1, In HP, form LACP trunk with Fortigate:
3500yl(config)#trunk 2,10,15-16,18 Trk2 LACP
3500yl(config)# sh trunks
Load Balancing
Port | Name Type | Group Type
---- + -------------------------------- --------- + ----- -----
2 | To_ControlPC_ 100/1000T | Trk2 LACP
10 | Hen_Trunk 100/1000T | Trk2 LACP
15 | Reserved 100/1000T | Trk2 LACP
16 | Reserved2 100/1000T | Trk2 LACP
18 | MINE_trunk 100/1000T | Trk2 LACP
===As long as the interface is up, it will be list here.
3500yl(config)# sh vlan 901
Status and Counters - VLAN Information - Ports - VLAN 901
802.1Q VLAN ID : 901
Name : VLAN901
Status : Port-based
Voice : No
Jumbo : No
Port Information Mode Unknown VLAN Status
---------------- -------- ------------ ----------
5 Tagged Learn Up
6 Tagged Learn Up
7 Tagged Learn Up
8 Tagged Learn Up
11 Tagged Learn Up
19 Tagged Learn Up
21 Tagged Learn Up
22 Tagged Learn Up
23 Tagged Learn Up
24 Tagged Learn Up
A1 Tagged Learn Up
A4 Tagged Learn Up
Trk1 Untagged Learn Down
Trk2 Tagged Learn Up =====> FGT use default setting (Active)
1, In HP, form LACP trunk with Fortigate:
3500yl(config)#trunk 2,10,15-16,18 Trk2 LACP
3500yl(config)# sh trunks
Load Balancing
Port | Name Type | Group Type
---- + -------------------------------- --------- + ----- -----
2 | To_ControlPC_ 100/1000T | Trk2 LACP
10 | Hen_Trunk 100/1000T | Trk2 LACP
15 | Reserved 100/1000T | Trk2 LACP
16 | Reserved2 100/1000T | Trk2 LACP
18 | MINE_trunk 100/1000T | Trk2 LACP
===As long as the interface is up, it will be list here.
3500yl(config)# sh vlan 901
Status and Counters - VLAN Information - Ports - VLAN 901
802.1Q VLAN ID : 901
Name : VLAN901
Status : Port-based
Voice : No
Jumbo : No
Port Information Mode Unknown VLAN Status
---------------- -------- ------------ ----------
5 Tagged Learn Up
6 Tagged Learn Up
7 Tagged Learn Up
8 Tagged Learn Up
11 Tagged Learn Up
19 Tagged Learn Up
21 Tagged Learn Up
22 Tagged Learn Up
23 Tagged Learn Up
24 Tagged Learn Up
A1 Tagged Learn Up
A4 Tagged Learn Up
Trk1 Untagged Learn Down
Trk2 Tagged Learn Up =====> FGT use default setting (Active)
Wednesday, October 8, 2008
QinQ
5003A:
Custom -------(f2)5003A(f3)-------serviceProvider
BCM.1> dtag mode xe14 external
BCM.1> dtag mode xe15 internal
BCM.1> dtag show
port 1:xe0 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe1 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe2 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe3 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe4 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe5 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe6 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe7 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe8 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe9 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe10 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe11 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe12 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe13 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe14 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe15 double tag mode internal (service provider), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe16 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe17 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe18 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe19 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
BCM.1> exit
5003A-L-87 # sh switch fabric-channel interface f2
config switch fabric-channel interface
edit "f2"
set native-vlan 1901
set allowed-vlans 1,101-200,901-910,1901
next
end
5003A-L-87 # sh switch fabric-channel interface f3
config switch fabric-channel interface
edit "f3"
set allowed-vlans 1,60,901,1901
next
end
On FortiOS side, by default vlanforward is enabled that means when the interface got 802.1q packet and no vlan interface under it, it will just forward out to other interface.
==============================
Cisco 3550
interface FastEthernet0/21
switchport access vlan 1901
switchport mode dot1q-tunnel
HP:
As HP procurve got double vlan packet, it will change the vlanID to 4096 and that is.
In another word, it does not support dtag.
Avalanche can send out DTAG traffic, but only on client side.
5003A:
Custom -------(f2)5003A(f3)-------serviceProvider
BCM.1> dtag mode xe14 external
BCM.1> dtag mode xe15 internal
BCM.1> dtag show
port 1:xe0 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe1 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe2 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe3 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe4 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe5 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe6 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe7 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe8 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe9 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe10 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe11 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe12 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe13 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe14 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe15 double tag mode internal (service provider), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe16 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe17 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe18 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
port 1:xe19 double tag mode external (customer), tpid 0x8100
BCM.1> exit
5003A-L-87 # sh switch fabric-channel interface f2
config switch fabric-channel interface
edit "f2"
set native-vlan 1901
set allowed-vlans 1,101-200,901-910,1901
next
end
5003A-L-87 # sh switch fabric-channel interface f3
config switch fabric-channel interface
edit "f3"
set allowed-vlans 1,60,901,1901
next
end
On FortiOS side, by default vlanforward is enabled that means when the interface got 802.1q packet and no vlan interface under it, it will just forward out to other interface.
==============================
Cisco 3550
interface FastEthernet0/21
switchport access vlan 1901
switchport mode dot1q-tunnel
HP:
As HP procurve got double vlan packet, it will change the vlanID to 4096 and that is.
In another word, it does not support dtag.
Avalanche can send out DTAG traffic, but only on client side.
Wednesday, October 1, 2008
Howto Windows AD
bbs.winos.cn
http://bbs.winos.cn/thread-39787-1-3.html
C:/net use //172.18.9.203/software * /user:zkang
After create GPO, Group Policy Object, we need to go to its' own property and apply this GPO to certain user groups which will be used.
bbs.winos.cn
http://bbs.winos.cn/thread-39787-1-3.html
C:/net use //172.18.9.203/software * /user:zkang
After create GPO, Group Policy Object, we need to go to its' own property and apply this GPO to certain user groups which will be used.
Tuesday, September 23, 2008
LAB 1
======================================= Tips ===================================
1.2
.In one switch, protected port doesn't forward traffic to any other protected port
interface FastEthernet0/23
switchport access vlan 13
switchport protected
!
interface FastEthernet0/24
switchport protected
1.6
.inter atm 0/0.1 point-to-point ==> Frame Mode
inter atm 0/0.1 mpls ==> Cell mode
2.3
."not able to intercept any ospf traffic" ====> (unicast) neighbor xxxx
4.4 mpls traffic engineering, ospf, in case of link fail
CiscoSample
4 steps:
--a, routing protocal: ON all core router
mpls traffic-eng area X
mpls traffic-eng router-id LoopbackN
--b, enable mpls engineering on ALL interface: On all core router
mpls traffic-engineering tunnel
--c, enable rsvp on ALL interface: On all core router
ip rsvp bandwidth
--d, tunnel interface: On tunnel head and tail Only
tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng
5.4 R5 announce R8 to vpn_A by importing and exporting its RT.
5.5 VRF aware NAT: R5 translate VPN_A address to others.
interface Ethernet0/0
ip nat outside
!i
nterface Serial0/0.1 point-to-point
ip nat inside
ip nat inside source route-map NAT_FROM_BB2 interface Ethernet0/0 vrf
VPN_A overload
ip nat inside source route-map NAT_FROM_R7 interface Loopback0 vrf
VPN_A overload
5.6 R5 VPN_B only import R6's RT, it is why R6 and R4 use different RT for VPN_A.
6.1 R3 disseminates RP to group mappings and accepts all PIM register messages throughout the multicast network.
i
p pim bsr-candidate Loopback0 0
ip pim rp-candidate Loopback0
6.2 Core network use group 239.0.100.1 to carry VPN_A's multicast
ip vrf VPN_A
mdt default 239.100.0.1
b, ip mroute:
Usage Guidelines
This command allows you to statically configure where multicast sources are located (even though the unicast routing table shows something different).
7. QoS
MPLS exp bit
8. Security
9. System Management
R4:
mpls traffic-eng logging lsp setups
mpls traffic-eng logging lsp teardowns
!l
ogging 131.1.26.100
10. IP service.
R1:
no mpls ip propagate-ttl forwarded
1, NAT aware VRF
2, Multicast VRF
==============1, NAT Aware VRF ===========================

5.5 NAT Integration with MPLS VPNs
NAT could be implemented on the PE route in the following scenarios:
•Service point—Shared access can be from a generic interface or from a VPN interface.
•NAT point—NAT can be configured on the PE router that is directly connected to the shared access gateway, or on the PE router that is not directly connected to the shared access gateway.
•NAT interface—The shared access gateway interface most often is configured as the outside interface of NAT. The inside interface of NAT can be either the PE-CE interface of a VPN, the interface to the MPLS backbone, or both. The shared access gateway interface can also be configured as the inside interface.
•Routing type—Common service can be Internet connectivity or a common server. For Internet connectivity, a default route should be propagated to all the VPN customers that use the service. For common server access, a static or dynamically learned route should be propagated to the VPN customers.
•NAT configuration—NAT can have different configurations: static, dynamic, pool/interface overloading, and route-map.
ip nat inside source
To enable Network Address Translation (NAT) of the inside source address, use the ip nat inside source command in global configuration mode. To remove the static translation or remove the dynamic association to a pool, use the no form of this command.
ip nat inside source {list {access-list-number | access-list-name} | route-map name} {interface type number | pool pool-name} vrf vrf-name [overload]
no ip nat inside source {list {access-list-number | access-list-name} | route-map name} {interface type number | pool pool-name} vrf vrf-name [overload]
Static NAT
ip nat inside source {static {local-ip global-ip} vrf vrf-name [extendable] [no-alias] [no-payload] [route-map] [redundancy group-name]
no ip nat inside source {static {local-ip global-ip} vrf vrf-name [extendable] [no-alias] [no-payload] [route-map] [redundancy group-name]
Port Static NAT
ip nat inside source {static {tcp | udp local-ip local-port global-ip global-port} [extendable] [no-alias] [no-payload]
no ip nat inside source {static {tcp | udp local-ip local-port global-ip global-port} [extendable] [no-alias] [no-payload]
Network Static NAT
ip nat inside source {static {network local-network global-network mask} [extendable] [no-alias] [no-payload]
no ip nat inside source {static {network local-network global-network mask} [extendable] [no-alias] [no-payload]
Syntax Description
list access-list-number
Standard IP access list number. Packets with source addresses that pass the access list are dynamically translated using global addresses from the named pool.
list access-list-name
Name of a standard IP access list. Packets with source addresses that pass the access list are dynamically translated using global addresses from the named pool.
route-map name
Specifies the named route-map.
interface type
Specifies the interface type for the global address.
interface number
Specifies the interface number for the global address.
pool pool-name
Specifies the pool from which global IP addresses are allocated dynamically.
vrf vrf-name
Associates the NAT translation rule with a particular VPN routing/forwarding (VRF) instance.
overload
(Optional) Enables the router to use one global address for many local addresses. When overloading is configured, the TCP or User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port number of each inside host distinguishes between the multiple conversations using the same local IP address.
================== 2, Multicast VRF ================
a, sample configure from Cisco

What's RP?
RPs are used by senders to a multicast group to announce their existence and by receivers of multicast packets to learn about new senders.
The RP address is used by first hop routers to send PIM register messages on behalf of a host sending a packet to the group. The RP address is also used by last hop routers to send PIM join and prune messages to the RP to inform it about group membership. You must configure the RP address on all routers (including the RP router).
Router(config)# ip pim rp-address rp-address [access-list] [override]
Auto-RP
Configuring Auto-RP
Auto-RP is a feature that automates the distribution of group-to-RP mappings in a PIM network. This feature has the following benefits:
•The use of multiple RPs within a network to serve different group ranges is easy.
•It allows load splitting among different RPs and arrangement of RPs according to the location of group participants.
•It avoids inconsistent, manual RP configurations that can cause connectivity problems.
Multiple RPs can be used to serve different group ranges or serve as backups of each other. To make Auto-RP work, a router must be designated as an RP-mapping agent, which receives the RP-announcement messages from the RPs and arbitrates conflicts. The RP-mapping agent then sends the consistent group-to-RP mappings to all other routers. Thus, all routers automatically discover which RP to use for the groups they support.
ip pim send-rp-announce type number scope ttl-value [group-list access-list] [interval seconds]
RP --|--(anounce RP)-----Mapping Agent------All Multicast router
RP --|
mapping agent:
Assigning the RP Mapping Agent
The RP mapping agent is the router that sends the authoritative discovery packets telling other routers which group-to-RP mapping to use. Such a role is necessary in the event of conflicts (such as overlapping group-to-RP ranges).
Router(config)# ip pim send-rp-discovery scope ttl-value
Auto-RP is a feature that automates the distribution of group-to-RP mappings in a PIM network. This feature has the following benefits:
•The use of multiple RPs within a network to serve different group ranges is easy.
•It allows load splitting among different RPs and arrangement of RPs according to the location of group participants.
•It avoids inconsistent, manual RP configurations that can cause connectivity problems.
BSR (bootstrap router)
Configuring Candidate BSRs
Configure one or more candidate BSRs. The routers to serve as candidate BSRs should be well connected and be in the backbone portion of the network, as opposed to the dialup portion of the network.
Router(config)# ip pim bsr-candidate type number hash-mask-length [priority]
Configure one or more candidate RPs. Similar to BSRs, the RPs should also be well connected and in the backbone portion of the network. An RP can serve the entire IP multicast address space or a portion of it. Candidate RPs send candidate RP advertisements to the BSR.
Router(config)# ip pim rp-candidate type number [group-list access-list] [priority value]
========================================
 v
v
======================================= Tips ===================================
1.2
.In one switch, protected port doesn't forward traffic to any other protected port
interface FastEthernet0/23
switchport access vlan 13
switchport protected
!
interface FastEthernet0/24
switchport protected
1.6
.inter atm 0/0.1 point-to-point ==> Frame Mode
inter atm 0/0.1 mpls ==> Cell mode
2.3
."not able to intercept any ospf traffic" ====> (unicast) neighbor xxxx
4.4 mpls traffic engineering, ospf, in case of link fail
CiscoSample
4 steps:
--a, routing protocal: ON all core router
mpls traffic-eng area X
mpls traffic-eng router-id LoopbackN
--b, enable mpls engineering on ALL interface: On all core router
mpls traffic-engineering tunnel
--c, enable rsvp on ALL interface: On all core router
ip rsvp bandwidth
--d, tunnel interface: On tunnel head and tail Only
tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng
5.4 R5 announce R8 to vpn_A by importing and exporting its RT.
5.5 VRF aware NAT: R5 translate VPN_A address to others.
interface Ethernet0/0
ip nat outside
!i
nterface Serial0/0.1 point-to-point
ip nat inside
ip nat inside source route-map NAT_FROM_BB2 interface Ethernet0/0 vrf
VPN_A overload
ip nat inside source route-map NAT_FROM_R7 interface Loopback0 vrf
VPN_A overload
5.6 R5 VPN_B only import R6's RT, it is why R6 and R4 use different RT for VPN_A.
6.1 R3 disseminates RP to group mappings and accepts all PIM register messages throughout the multicast network.
i
p pim bsr-candidate Loopback0 0
ip pim rp-candidate Loopback0
6.2 Core network use group 239.0.100.1 to carry VPN_A's multicast
ip vrf VPN_A
mdt default 239.100.0.1
b, ip mroute:
Usage Guidelines
This command allows you to statically configure where multicast sources are located (even though the unicast routing table shows something different).
7. QoS
MPLS exp bit
8. Security
9. System Management
R4:
mpls traffic-eng logging lsp setups
mpls traffic-eng logging lsp teardowns
!l
ogging 131.1.26.100
10. IP service.
R1:
no mpls ip propagate-ttl forwarded
1, NAT aware VRF
2, Multicast VRF
==============1, NAT Aware VRF ===========================

5.5 NAT Integration with MPLS VPNs
NAT could be implemented on the PE route in the following scenarios:
•Service point—Shared access can be from a generic interface or from a VPN interface.
•NAT point—NAT can be configured on the PE router that is directly connected to the shared access gateway, or on the PE router that is not directly connected to the shared access gateway.
•NAT interface—The shared access gateway interface most often is configured as the outside interface of NAT. The inside interface of NAT can be either the PE-CE interface of a VPN, the interface to the MPLS backbone, or both. The shared access gateway interface can also be configured as the inside interface.
•Routing type—Common service can be Internet connectivity or a common server. For Internet connectivity, a default route should be propagated to all the VPN customers that use the service. For common server access, a static or dynamically learned route should be propagated to the VPN customers.
•NAT configuration—NAT can have different configurations: static, dynamic, pool/interface overloading, and route-map.
ip nat inside source
To enable Network Address Translation (NAT) of the inside source address, use the ip nat inside source command in global configuration mode. To remove the static translation or remove the dynamic association to a pool, use the no form of this command.
ip nat inside source {list {access-list-number | access-list-name} | route-map name} {interface type number | pool pool-name} vrf vrf-name [overload]
no ip nat inside source {list {access-list-number | access-list-name} | route-map name} {interface type number | pool pool-name} vrf vrf-name [overload]
Static NAT
ip nat inside source {static {local-ip global-ip} vrf vrf-name [extendable] [no-alias] [no-payload] [route-map] [redundancy group-name]
no ip nat inside source {static {local-ip global-ip} vrf vrf-name [extendable] [no-alias] [no-payload] [route-map] [redundancy group-name]
Port Static NAT
ip nat inside source {static {tcp | udp local-ip local-port global-ip global-port} [extendable] [no-alias] [no-payload]
no ip nat inside source {static {tcp | udp local-ip local-port global-ip global-port} [extendable] [no-alias] [no-payload]
Network Static NAT
ip nat inside source {static {network local-network global-network mask} [extendable] [no-alias] [no-payload]
no ip nat inside source {static {network local-network global-network mask} [extendable] [no-alias] [no-payload]
Syntax Description
list access-list-number
Standard IP access list number. Packets with source addresses that pass the access list are dynamically translated using global addresses from the named pool.
list access-list-name
Name of a standard IP access list. Packets with source addresses that pass the access list are dynamically translated using global addresses from the named pool.
route-map name
Specifies the named route-map.
interface type
Specifies the interface type for the global address.
interface number
Specifies the interface number for the global address.
pool pool-name
Specifies the pool from which global IP addresses are allocated dynamically.
vrf vrf-name
Associates the NAT translation rule with a particular VPN routing/forwarding (VRF) instance.
overload
(Optional) Enables the router to use one global address for many local addresses. When overloading is configured, the TCP or User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port number of each inside host distinguishes between the multiple conversations using the same local IP address.
================== 2, Multicast VRF ================
a, sample configure from Cisco

What's RP?
RPs are used by senders to a multicast group to announce their existence and by receivers of multicast packets to learn about new senders.
The RP address is used by first hop routers to send PIM register messages on behalf of a host sending a packet to the group. The RP address is also used by last hop routers to send PIM join and prune messages to the RP to inform it about group membership. You must configure the RP address on all routers (including the RP router).
Router(config)# ip pim rp-address rp-address [access-list] [override]
Auto-RP
Configuring Auto-RP
Auto-RP is a feature that automates the distribution of group-to-RP mappings in a PIM network. This feature has the following benefits:
•The use of multiple RPs within a network to serve different group ranges is easy.
•It allows load splitting among different RPs and arrangement of RPs according to the location of group participants.
•It avoids inconsistent, manual RP configurations that can cause connectivity problems.
Multiple RPs can be used to serve different group ranges or serve as backups of each other. To make Auto-RP work, a router must be designated as an RP-mapping agent, which receives the RP-announcement messages from the RPs and arbitrates conflicts. The RP-mapping agent then sends the consistent group-to-RP mappings to all other routers. Thus, all routers automatically discover which RP to use for the groups they support.
ip pim send-rp-announce type number scope ttl-value [group-list access-list] [interval seconds]
RP --|--(anounce RP)-----Mapping Agent------All Multicast router
RP --|
mapping agent:
Assigning the RP Mapping Agent
The RP mapping agent is the router that sends the authoritative discovery packets telling other routers which group-to-RP mapping to use. Such a role is necessary in the event of conflicts (such as overlapping group-to-RP ranges).
Router(config)# ip pim send-rp-discovery scope ttl-value
Auto-RP is a feature that automates the distribution of group-to-RP mappings in a PIM network. This feature has the following benefits:
•The use of multiple RPs within a network to serve different group ranges is easy.
•It allows load splitting among different RPs and arrangement of RPs according to the location of group participants.
•It avoids inconsistent, manual RP configurations that can cause connectivity problems.
BSR (bootstrap router)
Configuring Candidate BSRs
Configure one or more candidate BSRs. The routers to serve as candidate BSRs should be well connected and be in the backbone portion of the network, as opposed to the dialup portion of the network.
Router(config)# ip pim bsr-candidate type number hash-mask-length [priority]
Configure one or more candidate RPs. Similar to BSRs, the RPs should also be well connected and in the backbone portion of the network. An RP can serve the entire IP multicast address space or a portion of it. Candidate RPs send candidate RP advertisements to the BSR.
Router(config)# ip pim rp-candidate type number [group-list access-list] [priority value]
========================================
 v
v
Wednesday, September 17, 2008
Traffic Engineering
1. Using MPLS TE in Real Life
2. Compare the RIB and FIB
3. LDP's 4 major function
4. Basic MPLS TE Tunnel Interface
5. Path-option command syntax
6. RSVP path setup
=============1. Using MPLS TE in Real Life ==============
Network engineering is manipulating your network to suit your traffic.v
Traffic engineering is manipulating your traffic to fit your network.
Traffic engineering, at its core, is the art of moving traffic around so that traffic from a congested link is moved onto the unused capacity on another link.
Using MPLS TE in Real Life
1, Optimizing your network utilization
2, Handling unexpected congestion
3, Handling link and node failures
=============>> 2. Compare the RIB and FIB <<================
7200a#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
Gateway of last resort is 7.1.5.1 to network 0.0.0.0
B 171.68.0.0/16 [200/0] via 12.12.12.12, 01:10:44
3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
FIB
7200a#show ip cef 171.68.0.0
171.68.0.0/16, version 69, cached adjacency to POS3/0
0 packets, 0 bytes, wccp tag 139
via 12.12.12.12, 0 dependencies, recursive
next hop 10.0.3.5, POS3/0 via 12.12.12.12/32
valid cached adjacency
============> 3. LDP's 4 major function <==============
LDP's Major Functions
LDP has four major functions:
Neighbor discovery
Session establishment and maintenance
Label advertisement
Notification
Neighbor Discovery
Like most other network protocols, LDP has the concept of neighbors. LDP uses UDP/TCP ports 646 for discovery. LDP has two different types of neighbors:
Directly connected neighbors— These neighbors have a Layer 2 connection between them. So, routers that are connected by any Layer 2 link—whether a POS link, an ATM PVC, an Ethernet connection, or a DS-3 interface—are considered directly connected for LDP. Neighbors connected by a logical connection such as GRE tunnel are also considered directly connected. The basic commonality over such connections is the fact that a neighbor is one IP hop away.
Non-directly connected neighbors— These neighbors do not have a Layer 2 connection between them. More importantly, these neighbors are several IP hops away. Routers that are connected to each other by MPLS traffic engineering tunnels and that have LDP enabled on them are considered non-directly connected. Such an LDP session is called a targeted or directed LDP session.
The only difference between directly and non-directly connected neighbors is in how they discover each other. LSRs discover directly connected neighbors by sending LDP hello messages encapsulated in UDP to the 224.0.0.2 multicast address (all routers on a subnet). These packets are known as hello messages.
Non-directly connected neighbors can't be reached through a multicast UDP packet. So, the same hello messages are sent as unicasts (also to UDP port 646). This requires that an LSR know ahead of time who it wants to have as a non-directly connected neighbor. This can be achieved through configuration.
===========< 4. Basic MPLS TE Tunnel Interface >===========
Most commands that modify the behavior of a TE tunnel headend are configured on traffic engineering tunnels, as opposed to physical interfaces or in the global configuration. All the commands configured on a traffic engineering tunnel start with tunnel mpls traffic-eng. Keep this in mind as you learn more about how to configure tunnel interfaces.
interface Tunnel0
ip unnumbered Loopback0
tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng
tunnel destination destination-ip
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 dynamic
Explaination:
interface Tunnel0: MPLS Traffic Engineering tunnels are represented as tunnel interfaces in the Cisco IOS Software. From this perspective, an MPLS Traffic Engineering tunnel is no different from a GRE tunnel or any other kind of tunnel you can configure.
ip unnumbered Loopback0: Cisco IOS Software does not forward traffic down an interface without an IP address on it, so you need to assign an IP address to the MPLS Traffic Engineering tunnel you've just created. However, because TE tunnels are unidirectional and don't have the concept of a link neighbor with which to communicate, it's a waste of addresses to put an additional IP address on the interface.
tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng: Tells the Cisco IOS Software that this tunnel interface is an MPLS Traffic Engineering tunnel. Other possible tunnel modes are GRE, DVMRP, and so on.
tunnel destination destination-ip: Tells the Cisco IOS Software what the tunnel's endpoint is. The IP address specified here is the MPLS Traffic Engineering RID (more on that later) of the router to which you want to build a tunnel. The destination-ip in this case is the Loopback0 interface on the tunnel's tailend router.
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 dynamic Tells the Cisco IOS Software how to generate the path from the tunnel headend to the tunnel tail. This command is covered in more detail in Chapter 4.
=================== 5. path-optin command syntax ================
Table 4-16. tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option Command Syntax Explanation Keyword Description
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option preference Defines a path-option for this tunnel. preference is a number from 1 to 1000. Different path-option values are tried in preference order from lowest to highest.
dynamic: Tells the router that it is supposed to calculate the best path that fits the configured tunnel constraints, such as band-width and affinity bits.
explicit: Allows you to specify an explicit path (configured separately) across the network that the tunnel will take. The explicit path also has to match the configured tunnel constraints, and the tunnel headend will check the explicit path to make sure that these constraints are met before trying to signal the path.
identifier identifier | name name: When explicit paths are created, they're given names or numbers. This option specifies which path option to consider.
lockdown: Configuring lockdown prevents a TE tunnel from being periodically reoptimized. See the later section "Tunnel Reoptimization."
=========== 6. RSVP path setup ================
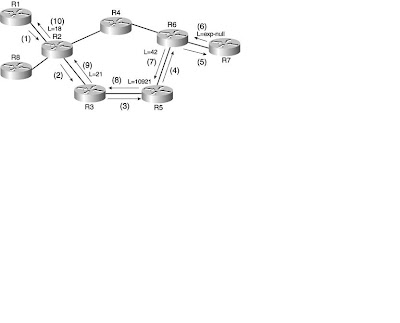
1, R1 sends a Path message to R2. R2 receives the path message, checks to make sure that the message is syntactically correct, and checks with the TE Link Manager to make sure that the bandwidth R1 requested is actually available. If anything is wrong (the Path message is incorrectly formed or is asking for more bandwidth than R2 can provide), R2 sends an error message back to R1. Assuming that everything is good, move on to Step 2.
2, R2 sends a Path message to R3. R3 goes through the same verification of the Path message that R2 did.
3, R3 sends a Path message to R5; the same checks happen.
4, R5 sends a Path message to R6; the same checks happen.
5, R6 sends a Path message to R7; the same checks happen.
6, R7, being the tunnel tail, sends a Resv message to R6. This Resv message indicates the label R7 would like to see on the packet for this tunnel; because R7 is the tail, it sends implicit-null.
7, R6 sends a Resv message to R5 and indicates that it wants to see incoming label 42 for this tunnel. This means that when R6 receives label 42, it removes that label (because of implicit-null) and sends the packet toward R7.
8, R5 sends a Resv message to R3, signalling label 10921. When R5 receives a packet with label 10921, it swaps that label for label 42 and sends the packet to R6.
9, R3 sends a Resv message to R2, signalling label 21.
10, R2 sends a Resv message to R1, signalling label 18.
At this point, R1 is done. It has received a Resv message for the tunnel to R7 it set up, and it knows which outgoing label to use. The Tunnel interface on R1 now comes up/up (until this point, the Tunnel interface is up/down).
1. Using MPLS TE in Real Life
2. Compare the RIB and FIB
3. LDP's 4 major function
4. Basic MPLS TE Tunnel Interface
5. Path-option command syntax
6. RSVP path setup
=============1. Using MPLS TE in Real Life ==============
Network engineering is manipulating your network to suit your traffic.v
Traffic engineering is manipulating your traffic to fit your network.
Traffic engineering, at its core, is the art of moving traffic around so that traffic from a congested link is moved onto the unused capacity on another link.
Using MPLS TE in Real Life
1, Optimizing your network utilization
2, Handling unexpected congestion
3, Handling link and node failures
=============>> 2. Compare the RIB and FIB <<================
7200a#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
Gateway of last resort is 7.1.5.1 to network 0.0.0.0
B 171.68.0.0/16 [200/0] via 12.12.12.12, 01:10:44
3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
FIB
7200a#show ip cef 171.68.0.0
171.68.0.0/16, version 69, cached adjacency to POS3/0
0 packets, 0 bytes, wccp tag 139
via 12.12.12.12, 0 dependencies, recursive
next hop 10.0.3.5, POS3/0 via 12.12.12.12/32
valid cached adjacency
============> 3. LDP's 4 major function <==============
LDP's Major Functions
LDP has four major functions:
Neighbor discovery
Session establishment and maintenance
Label advertisement
Notification
Neighbor Discovery
Like most other network protocols, LDP has the concept of neighbors. LDP uses UDP/TCP ports 646 for discovery. LDP has two different types of neighbors:
Directly connected neighbors— These neighbors have a Layer 2 connection between them. So, routers that are connected by any Layer 2 link—whether a POS link, an ATM PVC, an Ethernet connection, or a DS-3 interface—are considered directly connected for LDP. Neighbors connected by a logical connection such as GRE tunnel are also considered directly connected. The basic commonality over such connections is the fact that a neighbor is one IP hop away.
Non-directly connected neighbors— These neighbors do not have a Layer 2 connection between them. More importantly, these neighbors are several IP hops away. Routers that are connected to each other by MPLS traffic engineering tunnels and that have LDP enabled on them are considered non-directly connected. Such an LDP session is called a targeted or directed LDP session.
The only difference between directly and non-directly connected neighbors is in how they discover each other. LSRs discover directly connected neighbors by sending LDP hello messages encapsulated in UDP to the 224.0.0.2 multicast address (all routers on a subnet). These packets are known as hello messages.
Non-directly connected neighbors can't be reached through a multicast UDP packet. So, the same hello messages are sent as unicasts (also to UDP port 646). This requires that an LSR know ahead of time who it wants to have as a non-directly connected neighbor. This can be achieved through configuration.
===========< 4. Basic MPLS TE Tunnel Interface >===========
Most commands that modify the behavior of a TE tunnel headend are configured on traffic engineering tunnels, as opposed to physical interfaces or in the global configuration. All the commands configured on a traffic engineering tunnel start with tunnel mpls traffic-eng. Keep this in mind as you learn more about how to configure tunnel interfaces.
interface Tunnel0
ip unnumbered Loopback0
tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng
tunnel destination destination-ip
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 dynamic
Explaination:
interface Tunnel0: MPLS Traffic Engineering tunnels are represented as tunnel interfaces in the Cisco IOS Software. From this perspective, an MPLS Traffic Engineering tunnel is no different from a GRE tunnel or any other kind of tunnel you can configure.
ip unnumbered Loopback0: Cisco IOS Software does not forward traffic down an interface without an IP address on it, so you need to assign an IP address to the MPLS Traffic Engineering tunnel you've just created. However, because TE tunnels are unidirectional and don't have the concept of a link neighbor with which to communicate, it's a waste of addresses to put an additional IP address on the interface.
tunnel mode mpls traffic-eng: Tells the Cisco IOS Software that this tunnel interface is an MPLS Traffic Engineering tunnel. Other possible tunnel modes are GRE, DVMRP, and so on.
tunnel destination destination-ip: Tells the Cisco IOS Software what the tunnel's endpoint is. The IP address specified here is the MPLS Traffic Engineering RID (more on that later) of the router to which you want to build a tunnel. The destination-ip in this case is the Loopback0 interface on the tunnel's tailend router.
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option 10 dynamic Tells the Cisco IOS Software how to generate the path from the tunnel headend to the tunnel tail. This command is covered in more detail in Chapter 4.
=================== 5. path-optin command syntax ================
Table 4-16. tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option Command Syntax Explanation Keyword Description
tunnel mpls traffic-eng path-option preference Defines a path-option for this tunnel. preference is a number from 1 to 1000. Different path-option values are tried in preference order from lowest to highest.
dynamic: Tells the router that it is supposed to calculate the best path that fits the configured tunnel constraints, such as band-width and affinity bits.
explicit: Allows you to specify an explicit path (configured separately) across the network that the tunnel will take. The explicit path also has to match the configured tunnel constraints, and the tunnel headend will check the explicit path to make sure that these constraints are met before trying to signal the path.
identifier identifier | name name: When explicit paths are created, they're given names or numbers. This option specifies which path option to consider.
lockdown: Configuring lockdown prevents a TE tunnel from being periodically reoptimized. See the later section "Tunnel Reoptimization."
=========== 6. RSVP path setup ================

1, R1 sends a Path message to R2. R2 receives the path message, checks to make sure that the message is syntactically correct, and checks with the TE Link Manager to make sure that the bandwidth R1 requested is actually available. If anything is wrong (the Path message is incorrectly formed or is asking for more bandwidth than R2 can provide), R2 sends an error message back to R1. Assuming that everything is good, move on to Step 2.
2, R2 sends a Path message to R3. R3 goes through the same verification of the Path message that R2 did.
3, R3 sends a Path message to R5; the same checks happen.
4, R5 sends a Path message to R6; the same checks happen.
5, R6 sends a Path message to R7; the same checks happen.
6, R7, being the tunnel tail, sends a Resv message to R6. This Resv message indicates the label R7 would like to see on the packet for this tunnel; because R7 is the tail, it sends implicit-null.
7, R6 sends a Resv message to R5 and indicates that it wants to see incoming label 42 for this tunnel. This means that when R6 receives label 42, it removes that label (because of implicit-null) and sends the packet toward R7.
8, R5 sends a Resv message to R3, signalling label 10921. When R5 receives a packet with label 10921, it swaps that label for label 42 and sends the packet to R6.
9, R3 sends a Resv message to R2, signalling label 21.
10, R2 sends a Resv message to R1, signalling label 18.
At this point, R1 is done. It has received a Resv message for the tunnel to R7 it set up, and it knows which outgoing label to use. The Tunnel interface on R1 now comes up/up (until this point, the Tunnel interface is up/down).
Monday, September 15, 2008
Friday, September 12, 2008
Howto Config VG224
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 9111 bytes
!
version 12.4
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
!
stcapp ccm-group 1
stcapp
!
!
voice-card 0
!
!
!
!
!
voice service voip
fax protocol none
modem passthrough nse codec g711alaw redundancy
!
archive
log config
hidekeys
!
!
class-map match-any CALL_SIGNALLING
description ***Call Signalling Class Map***
match access-group name CALL_SIGNALLING
class-map match-any VOICE
description ***Voice Media Class Map***
match access-group name VOICE
!
!
policy-map ABC_CLASSIFICATION
class VOICE
set dscp ef
priority percent 45
class CALL_SIGNALLING
set dscp cs3
bandwidth percent 5
class class-default
set dscp default
fair-queue
random-detect
!
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 1.1.1.224 255.255.255.0
no ip redirects
no ip proxy-arp
duplex half
speed 100
arp timeout 3600
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
!
dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit
!
control-plane
!
!
voice-port 2/0
mwi
ren 3
disconnect-ack
loss-plan plan4
disc_pi_off
input gain 10
output attenuation 10
compand-type a-law
playout-delay minimum low
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
timing digit 53
music-threshold -50
bearer-cap Speech
station-id name ashwin
station-id number 200
caller-id enable
!
voice-port 2/1
mwi
ren 3
disconnect-ack
loss-plan plan4
disc_pi_off
input gain 10
output attenuation 10
compand-type a-law
playout-delay minimum low
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
timing digit 53
music-threshold -50
bearer-cap Speech
station-id name ashwix
station-id number 201
caller-id enable
!
voice-port 2/2
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
!
voice-port 2/3
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
!
voice-port 2/4
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
!
voice-port 2/5
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/5***
!
voice-port 2/6
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/6***
!
voice-port 2/7
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/7***
!
voice-port 2/8
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/8***
!
voice-port 2/9
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/9***
!
voice-port 2/10
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/10***
!
voice-port 2/11
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/11***
!
voice-port 2/12
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/12***
!
voice-port 2/13
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/13***
!
voice-port 2/14
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/14***
!
voice-port 2/15
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/18***
!
voice-port 2/16
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/16***
!
voice-port 2/17
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/17***
!
voice-port 2/18
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/21***
!
voice-port 2/19
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/19***
!
voice-port 2/20
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
!
voice-port 2/21
!
voice-port 2/22
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/22***
!
voice-port 2/23
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
!
!
!
sccp local FastEthernet0/0
sccp ccm 1.1.1.99 identifier 1 version 4.1
sccp ip precedence 3
sccp
!
sccp ccm group 1
description ***CUCM Registration***
associate ccm 1 priority 1
switchback method graceful
!
!
dial-peer voice 99920 pots
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/0***
service stcapp
fax rate disable
port 2/0
!
END
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 9111 bytes
!
version 12.4
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
!
stcapp ccm-group 1
stcapp
!
!
voice-card 0
!
!
!
!
!
voice service voip
fax protocol none
modem passthrough nse codec g711alaw redundancy
!
archive
log config
hidekeys
!
!
class-map match-any CALL_SIGNALLING
description ***Call Signalling Class Map***
match access-group name CALL_SIGNALLING
class-map match-any VOICE
description ***Voice Media Class Map***
match access-group name VOICE
!
!
policy-map ABC_CLASSIFICATION
class VOICE
set dscp ef
priority percent 45
class CALL_SIGNALLING
set dscp cs3
bandwidth percent 5
class class-default
set dscp default
fair-queue
random-detect
!
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 1.1.1.224 255.255.255.0
no ip redirects
no ip proxy-arp
duplex half
speed 100
arp timeout 3600
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
!
dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit
!
control-plane
!
!
voice-port 2/0
mwi
ren 3
disconnect-ack
loss-plan plan4
disc_pi_off
input gain 10
output attenuation 10
compand-type a-law
playout-delay minimum low
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
timing digit 53
music-threshold -50
bearer-cap Speech
station-id name ashwin
station-id number 200
caller-id enable
!
voice-port 2/1
mwi
ren 3
disconnect-ack
loss-plan plan4
disc_pi_off
input gain 10
output attenuation 10
compand-type a-law
playout-delay minimum low
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
timing digit 53
music-threshold -50
bearer-cap Speech
station-id name ashwix
station-id number 201
caller-id enable
!
voice-port 2/2
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
!
voice-port 2/3
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
!
voice-port 2/4
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
!
voice-port 2/5
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/5***
!
voice-port 2/6
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/6***
!
voice-port 2/7
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/7***
!
voice-port 2/8
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/8***
!
voice-port 2/9
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/9***
!
voice-port 2/10
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/10***
!
voice-port 2/11
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/11***
!
voice-port 2/12
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/12***
!
voice-port 2/13
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/13***
!
voice-port 2/14
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/14***
!
voice-port 2/15
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/18***
!
voice-port 2/16
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/16***
!
voice-port 2/17
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/17***
!
voice-port 2/18
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/21***
!
voice-port 2/19
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/19***
!
voice-port 2/20
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
!
voice-port 2/21
!
voice-port 2/22
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
timeouts ringing infinity
timing hookflash-in 200 75
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/22***
!
voice-port 2/23
mwi
compand-type a-law
cptone GB
timeouts interdigit 5
!
!
!
sccp local FastEthernet0/0
sccp ccm 1.1.1.99 identifier 1 version 4.1
sccp ip precedence 3
sccp
!
sccp ccm group 1
description ***CUCM Registration***
associate ccm 1 priority 1
switchback method graceful
!
!
dial-peer voice 99920 pots
description ***VG224 FXS Port 2/0***
service stcapp
fax rate disable
port 2/0
!
END
Thursday, September 11, 2008
Lab Equipment and IOS Versionv
* 2600 series routers * IOS 12.2T (ENTERPRISE PLUS/H323 MCM)
* 3600 series routers * IOS 12.3T (ENTERPRISE PLUS/H323 MCM)
* 3700 series routers * IOS 12.3T (ENTERPRISE PLUS/H323 MCM)
* 7200 series routers * IOS 12.3T (ENTERPRISE PLUS/H323 MCM)
* Catalyst 3550 series switch * IOS 12.3T (ENTERPRISE PLUS/H323 MCM)
* 2600 series routers * IOS 12.2T (ENTERPRISE PLUS/H323 MCM)
* 3600 series routers * IOS 12.3T (ENTERPRISE PLUS/H323 MCM)
* 3700 series routers * IOS 12.3T (ENTERPRISE PLUS/H323 MCM)
* 7200 series routers * IOS 12.3T (ENTERPRISE PLUS/H323 MCM)
* Catalyst 3550 series switch * IOS 12.3T (ENTERPRISE PLUS/H323 MCM)
Monday, September 8, 2008
Howto IPV6 on XP, FortiOS
Compare V4 and V6
Ipv4 IPV6
Ethernet II: type field=0x800 Type field=0x86DD
Address: 32 bits in length 128 bits in length
Public address Global unicast address: 2000::/3
169.254.0.0/16 (address autoconfig process) Link local address: FE80::/64
Private address Site local address: FEC0::/64
ARP request(broadcast) multicast (ff02, neighbor solicitation)
arp reply (unicast) unicast (neighbor advertisement)
Note: If use link local address to test, the command need to specify the port:
FGT#exe ping6 -I port1 fe80::1
1, XP =>172.18.9.28
a, C:>ipv6 install
b, C:>ipv6 if
c, C:>ping6 ::1
d, C:>netsh interfa ipv6 add address 172.18.9.28 2001:0:0:89::28
e, C:>netsh interface ipv6 show interface
f, C:>netsh interface ipv6 add route ::/0 172.18.9.28 2001:0:0:89::1 store=persistent
2, FortiOS
config system interface
edit "vlan89"
set vdom "root"
set ip 172.18.9.86 255.255.255.0
set allowaccess ping https ssh snmp http telnet
config ipv6
set ip6-address 2001:0:0:89::36/64
set ip6-allowaccess ping
end
set interface "internal"
set vlanid 89
next
end
config router static6
edit 1
set device "port1"
set gateway 2001:0:0:1::37
next
end
3, Linux ==>172.18.9.13
http://tldp.org/HOWTO/Linux+IPv6-HOWTO/x1052.html
# /sbin/ifconfig inet6 add ipv6address/prefixlength
# /sbin/route -A inet6 add 2000::/3 gw 2001:0db8:0:f101::1
# /sbin/route -A inet6 del 2000::/3 gw 2001:0db8:0:f101::1
Compare V4 and V6
Ipv4 IPV6
Ethernet II: type field=0x800 Type field=0x86DD
Address: 32 bits in length 128 bits in length
Public address Global unicast address: 2000::/3
169.254.0.0/16 (address autoconfig process) Link local address: FE80::/64
Private address Site local address: FEC0::/64
ARP request(broadcast) multicast (ff02, neighbor solicitation)
arp reply (unicast) unicast (neighbor advertisement)
Note: If use link local address to test, the command need to specify the port:
FGT#exe ping6 -I port1 fe80::1
1, XP =>172.18.9.28
a, C:>ipv6 install
b, C:>ipv6 if
c, C:>ping6 ::1
d, C:>netsh interfa ipv6 add address 172.18.9.28 2001:0:0:89::28
e, C:>netsh interface ipv6 show interface
f, C:>netsh interface ipv6 add route ::/0 172.18.9.28 2001:0:0:89::1 store=persistent
2, FortiOS
config system interface
edit "vlan89"
set vdom "root"
set ip 172.18.9.86 255.255.255.0
set allowaccess ping https ssh snmp http telnet
config ipv6
set ip6-address 2001:0:0:89::36/64
set ip6-allowaccess ping
end
set interface "internal"
set vlanid 89
next
end
config router static6
edit 1
set device "port1"
set gateway 2001:0:0:1::37
next
end
3, Linux ==>172.18.9.13
http://tldp.org/HOWTO/Linux+IPv6-HOWTO/x1052.html
# /sbin/ifconfig
# /sbin/route -A inet6 add 2000::/3 gw 2001:0db8:0:f101::1
# /sbin/route -A inet6 del 2000::/3 gw 2001:0db8:0:f101::1
Friday, September 5, 2008
Howto callmanager call flow
The following steps outline what happens within the cluster when a call is placed to a destination outside the cluster. For example, let's assume the call is being placed to the pizza place down the street.
Step 1. The caller dials the phone number of the pizza place.
Step 2. CallManager looks at those digits and finds a pattern that matches it. If it finds multiple patterns that match, it uses the closest (the one with the fewest possible matches).
Step 3. The pattern that the dialed number matches points to a route list that in turn points to one or more route groups.
Step 4. The route list sends the call to the first route group in it's list.
Step 5. The route group points to one or more gateways and sends the call to the first gateway in the group.
Step 6. If the gateway is unable to handle the call, the route group sends the call to the next gateway in it's list if there is one.
Step 7. If no other gateway exists in the group or if the last gateway in the group is unable to route the call, the call is returned to the route list and the route list sends the call to the next route group in the list.
Step 8. The next route group sends the call to the first gateway in the group.
Step 9. After the call reaches a gateway that is able to handle the call, the call is sent out of the system using that gateway.
Step 10. If no gateway is available, the call fails.

Understanding Route Groups and Route Lists
The job of a route group is to send the call to the gateway or gateways to which it points. The route group sends the call to the first gateway in the group, and if that gateway is unable to handle the call, the route group sends the call to the next gateway in the group. This process is repeated until a gateway in the list is identified that is able to handle the call, or there are no more gateways in the group. If the route group is unable to find an available gateway, the call is returned to the route list.
The job of a route list is to send the call to a route group, which in turn sends the call to a gateway. In the example shown in Figure 4-2, the call is first routed across the wide-area network (WAN). If that path is unable to accommodate the call, it is routed to the PSTN. As you can see, depending on which path the call takes, a different number of digits need to be sent. If the call is sent across the Inter-Cluster Trunk (ICT), only five digits are needed, assuming that the remote cluster is using five digit directory numbers. However, if the call goes across the PSTN, 11 digits are needed. To accomplish this, digit manipulation must take place. Digit manipulation occurs when a called (dialed) or calling (Caller ID) number is changed. In this case, the digit translation strips the required number of digits from the called number so that the call can be routed across the chosen path. Because the path the call takes is not known until it reaches the route group, the digit manipulation should take place there.

The following steps outline what happens within the cluster when a call is placed to a destination outside the cluster. For example, let's assume the call is being placed to the pizza place down the street.
Step 1. The caller dials the phone number of the pizza place.
Step 2. CallManager looks at those digits and finds a pattern that matches it. If it finds multiple patterns that match, it uses the closest (the one with the fewest possible matches).
Step 3. The pattern that the dialed number matches points to a route list that in turn points to one or more route groups.
Step 4. The route list sends the call to the first route group in it's list.
Step 5. The route group points to one or more gateways and sends the call to the first gateway in the group.
Step 6. If the gateway is unable to handle the call, the route group sends the call to the next gateway in it's list if there is one.
Step 7. If no other gateway exists in the group or if the last gateway in the group is unable to route the call, the call is returned to the route list and the route list sends the call to the next route group in the list.
Step 8. The next route group sends the call to the first gateway in the group.
Step 9. After the call reaches a gateway that is able to handle the call, the call is sent out of the system using that gateway.
Step 10. If no gateway is available, the call fails.

Understanding Route Groups and Route Lists
The job of a route group is to send the call to the gateway or gateways to which it points. The route group sends the call to the first gateway in the group, and if that gateway is unable to handle the call, the route group sends the call to the next gateway in the group. This process is repeated until a gateway in the list is identified that is able to handle the call, or there are no more gateways in the group. If the route group is unable to find an available gateway, the call is returned to the route list.
The job of a route list is to send the call to a route group, which in turn sends the call to a gateway. In the example shown in Figure 4-2, the call is first routed across the wide-area network (WAN). If that path is unable to accommodate the call, it is routed to the PSTN. As you can see, depending on which path the call takes, a different number of digits need to be sent. If the call is sent across the Inter-Cluster Trunk (ICT), only five digits are needed, assuming that the remote cluster is using five digit directory numbers. However, if the call goes across the PSTN, 11 digits are needed. To accomplish this, digit manipulation must take place. Digit manipulation occurs when a called (dialed) or calling (Caller ID) number is changed. In this case, the digit translation strips the required number of digits from the called number so that the call can be routed across the chosen path. Because the path the call takes is not known until it reaches the route group, the digit manipulation should take place there.

Monday, August 25, 2008
howto choose ROOT port or designated port?
A, Same Region
1. Lowest Root Bridge ID
2. Lowest Root Path Cost to Root Bridge
3. Lowest Sender Bridge ID
4. Lowest Sender Port ID
B, Different Region
1, Lowest Root Bridge ID
2, External pathcost
3, Regional Root ID
4, Internal Path Cost
5, Sender ID
6, Sender Port ID
7, Receiver Port ID

Test Case (Same Region):
1, L: Root for Instance 3, R: Root for instance 5, 0
default path cost, default bridge priority
Block: 3=>RF1 5=>LF1 0=>LF1
WHY: Lowest Sender Bridge ID. HP had lower MAC address than BridgeL.
2, Move 5 and 0's block point from LF1 to A1
By: Reduce the bridge L's priority.
WHY: Lowest Sender Bridge ID. Bridge L has lower priority.
3, Move 5 and 0's block point from A1 to LF1
By: Increase the path cost of LS1
A, Same Region
1. Lowest Root Bridge ID
2. Lowest Root Path Cost to Root Bridge
3. Lowest Sender Bridge ID
4. Lowest Sender Port ID
B, Different Region
1, Lowest Root Bridge ID
2, External pathcost
3, Regional Root ID
4, Internal Path Cost
5, Sender ID
6, Sender Port ID
7, Receiver Port ID

Test Case (Same Region):
1, L: Root for Instance 3, R: Root for instance 5, 0
default path cost, default bridge priority
Block: 3=>RF1 5=>LF1 0=>LF1
WHY: Lowest Sender Bridge ID. HP had lower MAC address than BridgeL.
2, Move 5 and 0's block point from LF1 to A1
By: Reduce the bridge L's priority.
WHY: Lowest Sender Bridge ID. Bridge L has lower priority.
3, Move 5 and 0's block point from A1 to LF1
By: Increase the path cost of LS1
Monday, August 18, 2008
Howto modify .tcc file to suit local lab
a, open the config file. Don't automatically reserve the port
b, Action->Relocate port->select port and next. use local chassis port to replace the original port

Howto do arp resolve on TestCenter
1, right click HOST icon and click start "ARP/ND"

By default, fixed frame lenth is 128 and that will cause performance issue. use big packet instead
howto create tcc file step-by-step
a, create Host
-> need to config host counts, ipv4 address range and gateway. Right click the host icon, you can send arp request to resolve gateway's mac.
b, create traffic.
-> schedule: Rate Base. we can specify percentage value
-> Traffic pattern: pair
-> tx: port1/2 rx: port 2/1
-> load: 50%
-> Destination: 192.168.200.0/24
-> Frame Length: change the default fix frame from 128 to 1500. Otherwise the packet lost will be found.
howto add UDP header to the traffic
1, without this header, FGT will drop some packets and the test result compromised.

Thursday, August 7, 2008
Sample: Useful proc in TCL
a, begin
#!/usr/bin/expect --
if {$argc == 0} {
puts stderr "Usage: changelink up|down"
exit 1
} else {
set status [lindex $argv 0]
}
b, check if the string exactly match. linkup and linkdown are the proc.
if { [string equal $status up] } {
linkup
} else {
linkdown
}
c, proc
proc linkdown { } {
spawn telnet 172.18.9.26
expect "#"
send "conf t\r"
expect "#"
send "inter f 0/11\r"
expect "#"
send "shut\r"
send "end\r"
#expect "#"
send "exit\r"
}
d, proc with parameter
proc clear_line {line} {
spawn telnet 172.18.9.29
expect "#"
send "clear line $line\r"
expect "confirm"
send "y\r"
exec sleep 2
expect "#"
send "exit\r"
expect "#"
}
e, proc used for firewall test
proc clear_line {line} {
spawn telnet 172.18.9.29
expect "#"
send "clear line $line\r"
expect "confirm"
send "y\r"
exec sleep 2
expect "#"
send "exit\r"
expect "#"
}
proc login_fw {2kline} {
spawn telnet 172.18.9.29 $2kline
#exec sleep 1
expect "]"
send "\r"
exec sleep 5
expect {
"login" {send "admin\r"
expect "assword"
send "\r"}
"#" {send "end\r"}
"assword" {send "aaa\r"
expect "login"
send "admin\r"
expect "assword"
send "\r"}
expect "#"
}
return $spawn_id
}
proc print_csum {serial} {
set spawn_id [login_fw $serial]
expect "#"
send "diag sys ha sh\r"
#exec sleep 5
expect "#"
set csumA $expect_out(buffer)
puts $csumA
}
clear_line $h3600
print_csum [expr 2000 + $h3600]
f, multispawn interactive
spawn telnet 172.18.9.29 200$h3600
set id1 $spawn_id
expect "]"
spawn telnet 172.18.9.29 200$l3600
set id2 $spawn_id
expect "]"
proc login_fw_id1 { } {
global id1
set spawn_id $id1
send "\r"
exec sleep 5
expect {
"login" {send "admin\r"
expect "assword"
send "\r"
expect "#"
}
"#" {send "end\r"
expect "#"}
"assword" {send "aaa\r"
expect "login"
send "admin\r"
expect "assword"
send "\r"}
expect "#"
}
return $spawn_id
}
proc login_fw_id2 { } {
global id2
set spawn_id $id2
send "\r"
exec sleep 5
expect {
"login" {send "admin\r"
expect "assword"
send "\r"
expect "#"
}
"#" {send "end\r"
expect "#"}
"assword" {send "aaa\r"
expect "login"
send "admin\r"
expect "assword"
send "\r"}
expect "#"
}
return $spawn_id
}
proc GetStatus-1 { } {
set spawn_id [login_fw_id1]
send "get sys status\r"
expect "#"
}
proc GetStatus-2 { } {
set spawn_id [login_fw_id2]
send "get sys status\r"
expect "#"
}
GetStatus-1
GetStatus-2
g, generate config file
#!/usr/bin/tclsh
set fileId [open ./1000vip.cfg w]
puts $fileId "config firewall vip"
for {set i 0} {$i < 4} {incr i} {
for {set j 1} {$j < 254} {incr j} {
set v [expr 254*$i+$j]
puts $fileId "edit jkvip$v
set extip 1.1.$i.$j
set mappedip 2.2.$i.$j
set extintf port1
next"
}
}
puts $fileId "end"
puts $fileId "config firewall vip"
for {set k 1} {$k <1001} {incr k} {
puts $fileId "delete jkvip$k"
}
puts $fileId "end"
close $fileId
h, send command from config file
proc sendcom {serial} {
set spawn_id [login_fw $serial]
expect "#"
send "conf g\r"
expect "#"
send " d debug cli 5\r"
expect "#"
set fileId [open ./250_intf_noip.cfg]
foreach line [split [read $fileId] \n] {
send "$line\r"
expect "#"
}
}
sendcom [expr 2000 + $line]
proc psleep {m} {
for {set n 0} {$n < [expr $m + 1]} {incr n 10} {
exec sleep 10
puts "$n...."
}
}
if {[string first "backup" $mainstatus] !=-1} { if mainstatus 中包括backup
puts " ################## Case 1: Everything same but SN.... Works #####################"
puts " ################## Case 1: L3600 with Higher SN wins #####################"
} else {
puts " ################## Case 1: Everything same but SN.... Fail #####################"
}
i, split a list and get one item which contain the certain string
proc print_csum {serial} {
set spawn_id [login_fw $serial]
expect "#"
send "diag sys ha sh\r"
#exec sleep 5
expect "#"
set csumA $expect_out(buffer)
puts $csumA
set l1 [split $csumA \r]
return [lsearch -inline $l1 *all*]
}
j, send command through telnet
spawn telnet 172.18.9.150
expect "login"
send "admin\r"
expect "assword:"
send "1\r"
expect "#"
while {1} {
set fileId [open $filea]
foreach line [split [read $fileId] \n] {
send "$line\r"
expect "#"
}
close $fileId
k, foreach
foreach value {126 125} {
spawn telnet 172.18.9.$value
expect "login"
send "admin\r"
expect "assword:"
send "\r"
expect "#"
============
How to generate random number between 0 and 100
set value [expr floor(rand()*100)]
puts "$value"
sleep $value
}
proc ransleep { } {
set value [expr floor(rand()*100)]
puts "$value"
sleep $value
}
a, begin
#!/usr/bin/expect --
if {$argc == 0} {
puts stderr "Usage: changelink up|down"
exit 1
} else {
set status [lindex $argv 0]
}
b, check if the string exactly match. linkup and linkdown are the proc.
if { [string equal $status up] } {
linkup
} else {
linkdown
}
c, proc
proc linkdown { } {
spawn telnet 172.18.9.26
expect "#"
send "conf t\r"
expect "#"
send "inter f 0/11\r"
expect "#"
send "shut\r"
send "end\r"
#expect "#"
send "exit\r"
}
d, proc with parameter
proc clear_line {line} {
spawn telnet 172.18.9.29
expect "#"
send "clear line $line\r"
expect "confirm"
send "y\r"
exec sleep 2
expect "#"
send "exit\r"
expect "#"
}
e, proc used for firewall test
proc clear_line {line} {
spawn telnet 172.18.9.29
expect "#"
send "clear line $line\r"
expect "confirm"
send "y\r"
exec sleep 2
expect "#"
send "exit\r"
expect "#"
}
proc login_fw {2kline} {
spawn telnet 172.18.9.29 $2kline
#exec sleep 1
expect "]"
send "\r"
exec sleep 5
expect {
"login" {send "admin\r"
expect "assword"
send "\r"}
"#" {send "end\r"}
"assword" {send "aaa\r"
expect "login"
send "admin\r"
expect "assword"
send "\r"}
expect "#"
}
return $spawn_id
}
proc print_csum {serial} {
set spawn_id [login_fw $serial]
expect "#"
send "diag sys ha sh\r"
#exec sleep 5
expect "#"
set csumA $expect_out(buffer)
puts $csumA
}
clear_line $h3600
print_csum [expr 2000 + $h3600]
f, multispawn interactive
spawn telnet 172.18.9.29 200$h3600
set id1 $spawn_id
expect "]"
spawn telnet 172.18.9.29 200$l3600
set id2 $spawn_id
expect "]"
proc login_fw_id1 { } {
global id1
set spawn_id $id1
send "\r"
exec sleep 5
expect {
"login" {send "admin\r"
expect "assword"
send "\r"
expect "#"
}
"#" {send "end\r"
expect "#"}
"assword" {send "aaa\r"
expect "login"
send "admin\r"
expect "assword"
send "\r"}
expect "#"
}
return $spawn_id
}
proc login_fw_id2 { } {
global id2
set spawn_id $id2
send "\r"
exec sleep 5
expect {
"login" {send "admin\r"
expect "assword"
send "\r"
expect "#"
}
"#" {send "end\r"
expect "#"}
"assword" {send "aaa\r"
expect "login"
send "admin\r"
expect "assword"
send "\r"}
expect "#"
}
return $spawn_id
}
proc GetStatus-1 { } {
set spawn_id [login_fw_id1]
send "get sys status\r"
expect "#"
}
proc GetStatus-2 { } {
set spawn_id [login_fw_id2]
send "get sys status\r"
expect "#"
}
GetStatus-1
GetStatus-2
g, generate config file
#!/usr/bin/tclsh
set fileId [open ./1000vip.cfg w]
puts $fileId "config firewall vip"
for {set i 0} {$i < 4} {incr i} {
for {set j 1} {$j < 254} {incr j} {
set v [expr 254*$i+$j]
puts $fileId "edit jkvip$v
set extip 1.1.$i.$j
set mappedip 2.2.$i.$j
set extintf port1
next"
}
}
puts $fileId "end"
puts $fileId "config firewall vip"
for {set k 1} {$k <1001} {incr k} {
puts $fileId "delete jkvip$k"
}
puts $fileId "end"
close $fileId
h, send command from config file
proc sendcom {serial} {
set spawn_id [login_fw $serial]
expect "#"
send "conf g\r"
expect "#"
send " d debug cli 5\r"
expect "#"
set fileId [open ./250_intf_noip.cfg]
foreach line [split [read $fileId] \n] {
send "$line\r"
expect "#"
}
}
sendcom [expr 2000 + $line]
proc psleep {m} {
for {set n 0} {$n < [expr $m + 1]} {incr n 10} {
exec sleep 10
puts "$n...."
}
}
if {[string first "backup" $mainstatus] !=-1} { if mainstatus 中包括backup
puts " ################## Case 1: Everything same but SN.... Works #####################"
puts " ################## Case 1: L3600 with Higher SN wins #####################"
} else {
puts " ################## Case 1: Everything same but SN.... Fail #####################"
}
i, split a list and get one item which contain the certain string
proc print_csum {serial} {
set spawn_id [login_fw $serial]
expect "#"
send "diag sys ha sh\r"
#exec sleep 5
expect "#"
set csumA $expect_out(buffer)
puts $csumA
set l1 [split $csumA \r]
return [lsearch -inline $l1 *all*]
}
j, send command through telnet
spawn telnet 172.18.9.150
expect "login"
send "admin\r"
expect "assword:"
send "1\r"
expect "#"
while {1} {
set fileId [open $filea]
foreach line [split [read $fileId] \n] {
send "$line\r"
expect "#"
}
close $fileId
k, foreach
foreach value {126 125} {
spawn telnet 172.18.9.$value
expect "login"
send "admin\r"
expect "assword:"
send "\r"
expect "#"
============
How to generate random number between 0 and 100
set value [expr floor(rand()*100)]
puts "$value"
sleep $value
}
proc ransleep { } {
set value [expr floor(rand()*100)]
puts "$value"
sleep $value
}
Saturday, August 2, 2008
U-Pick upick, u pick
U-Pick Farm
Crop Availability
Blueberry 3 Options:
a, No.5 BlueBerry Farm - follows organic methods, blueberries
7040 no.5 road.(Cross street of Granville), Richmond, BC V6Y2V2. Phone: 604-303-8733. Email us at: thiheng@hotmail.com. We are open July, August. Our hours are: We are open all through the July and August. Our Operation hours for U-Pick are: Fri-Sun = 11am-8pm, for Monday to Thursday are flexible. Please give us a call before you come. We follow organic methods, but are not yet certified. Payment: Cash, only.
b,# Blueberries U-Pick - Pick your own blueberries
18064-32 AVe , Surrey, BC V3S 0L5. Tel: (604) 290-4081. Open July, August and September. Call ahead to ensure berry availability.
c,# Forstbauer Natural Food Farm - ORGANIC pick your own certified organic produce such as blueberries, beets, blue lake pole beans, carrots, chard, dill cucumbers, kale, potatoes, pumpkins, summer and winter squash, zucchini
49350 Prairie Central Road, Chilliwack, BC. Phone: 604-794-3999. Email: farm@forstbauer.com. We are certified organic and bio dynamic. Learn about the principles of bio-dynamic farming. You are invited to experience harvesting your own , and many other vegetables. They also sell organically raised beef and have certified organic / bio-dynamic Okanagan fruits. This is an old listing; has anyone got a phone number for them?
d, # Krause Berry Farms - strawberries, blueberries and raspberries.
6179-248th Street, Aldegrove, BC, V4W 1C3, Canada. Phone: 604.856.5757. Email: info@krauseberryfarms.com. Directions: click here for a map and directions. Also prepicked blackberries and corn. A visitor writes: "They make there own pies, jams and syrups for people to buy. I went this morning and had a wonderful visit. Please put them on your list! I highly recommend them!" (UPDATED: July 31, 2008)
e,# Surrey Farms - pumpkins, strawberries, raspberries, blueberries
5180 – 152 Street, Surrey, BC. Phone: 604.574.1390. Fax: 604.574.1558. Open: every day from May 1 to October 31, 8 am to 7 pm. All types of vegetables in season; Okanagan fruit in season.
====================
http://www.westca.com/Forums/viewtopic/t=55890/lang=schinese.html
文章标题: Re: 请问哪儿可以采榛子? 时间: 2005-10-10 16:07
引用回复
8651 Glover Road, Fort Langley, BC
They still open for picking up hazelnuts until mildle of October.
The phone number there is 604-888-1640
16 AVE + 264 STREET, LANGLY, TEL: 518-6659 IT IS AN OLD ASIAN LADY'S FARM, 0.75/LB U PICK OR $2.00/LB TO BUY.
another one:
Organic Hazelnuts - $3 (Abbotsford)
Our Organic Hazelnuts are now falling and are ready for picking.
We offer picked hazelnuts for $3.00 per pound or you can come to the farm and do U-pick for $0.60 per pound.
We are located at 6624 Bradner Road in Abbotsford.
Check out our website for more information at garsidesfruitfarm.blogspot.com/ or email at garsidesfruitfarm@shaw.ca, or you can call us at 604.556.4273.
================
文章标题: 摘苹果 时间: 2008-9-27 22:20
引用回复
明天带小孩子去ABBOTSFORD的农场摘苹果, 想去的可以直接去玩,临时想起来, 就不组织了。
333 Gladwin Rd. | Abbotsford, BC | V2T 5Y1
www.applebarn.ca
=================
http://www.kelowna.ca/CM/Page91.aspx
=================
apricot (杏)
http://hillsideorchards.farmvisit.com/
Directions: We are located in the Sunny Okanogan Vally between Oliver & Osoyoos B.C. You can find us on Hwy. 97, across Rd#18. Look For the big YELLOW SIGN with a cartoon farmer on the top.
HWY 97 & rd #18 =====HWY 97 & rd 310

U-Pick Farm
Crop Availability
Blueberry 3 Options:
a, No.5 BlueBerry Farm - follows organic methods, blueberries
7040 no.5 road.(Cross street of Granville), Richmond, BC V6Y2V2. Phone: 604-303-8733. Email us at: thiheng@hotmail.com. We are open July, August. Our hours are: We are open all through the July and August. Our Operation hours for U-Pick are: Fri-Sun = 11am-8pm, for Monday to Thursday are flexible. Please give us a call before you come. We follow organic methods, but are not yet certified. Payment: Cash, only.
b,# Blueberries U-Pick - Pick your own blueberries
18064-32 AVe , Surrey, BC V3S 0L5. Tel: (604) 290-4081. Open July, August and September. Call ahead to ensure berry availability.
c,# Forstbauer Natural Food Farm - ORGANIC pick your own certified organic produce such as blueberries, beets, blue lake pole beans, carrots, chard, dill cucumbers, kale, potatoes, pumpkins, summer and winter squash, zucchini
49350 Prairie Central Road, Chilliwack, BC. Phone: 604-794-3999. Email: farm@forstbauer.com. We are certified organic and bio dynamic. Learn about the principles of bio-dynamic farming. You are invited to experience harvesting your own , and many other vegetables. They also sell organically raised beef and have certified organic / bio-dynamic Okanagan fruits. This is an old listing; has anyone got a phone number for them?
d, # Krause Berry Farms - strawberries, blueberries and raspberries.
6179-248th Street, Aldegrove, BC, V4W 1C3, Canada. Phone: 604.856.5757. Email: info@krauseberryfarms.com. Directions: click here for a map and directions. Also prepicked blackberries and corn. A visitor writes: "They make there own pies, jams and syrups for people to buy. I went this morning and had a wonderful visit. Please put them on your list! I highly recommend them!" (UPDATED: July 31, 2008)
e,# Surrey Farms - pumpkins, strawberries, raspberries, blueberries
5180 – 152 Street, Surrey, BC. Phone: 604.574.1390. Fax: 604.574.1558. Open: every day from May 1 to October 31, 8 am to 7 pm. All types of vegetables in season; Okanagan fruit in season.
====================
http://www.westca.com/Forums/viewtopic/t=55890/lang=schinese.html
文章标题: Re: 请问哪儿可以采榛子? 时间: 2005-10-10 16:07
引用回复
8651 Glover Road, Fort Langley, BC
They still open for picking up hazelnuts until mildle of October.
The phone number there is 604-888-1640
16 AVE + 264 STREET, LANGLY, TEL: 518-6659 IT IS AN OLD ASIAN LADY'S FARM, 0.75/LB U PICK OR $2.00/LB TO BUY.
another one:
Organic Hazelnuts - $3 (Abbotsford)
Our Organic Hazelnuts are now falling and are ready for picking.
We offer picked hazelnuts for $3.00 per pound or you can come to the farm and do U-pick for $0.60 per pound.
We are located at 6624 Bradner Road in Abbotsford.
Check out our website for more information at garsidesfruitfarm.blogspot.com/ or email at garsidesfruitfarm@shaw.ca, or you can call us at 604.556.4273.
================
文章标题: 摘苹果 时间: 2008-9-27 22:20
引用回复
明天带小孩子去ABBOTSFORD的农场摘苹果, 想去的可以直接去玩,临时想起来, 就不组织了。
333 Gladwin Rd. | Abbotsford, BC | V2T 5Y1
www.applebarn.ca
=================
http://www.kelowna.ca/CM/Page91.aspx
=================
apricot (杏)
http://hillsideorchards.farmvisit.com/
Directions: We are located in the Sunny Okanogan Vally between Oliver & Osoyoos B.C. You can find us on Hwy. 97, across Rd#18. Look For the big YELLOW SIGN with a cartoon farmer on the top.
HWY 97 & rd #18 =====HWY 97 & rd 310

美国旅游DIY(准备篇)
http://travel.westca.com/content/view/1031/76/
今年十月我和LG决定在他生日的时候乘飞机去美国洛杉矶,然后租车去大峡谷和拉斯维加斯游览。由于LG在启程之前一直出差在外,我只能负起了行程总策划的职责。
首先是订机票,经过反复比较,又因为我们有加航的里程积分卡,我在加航网上订了两人来回洛杉矶的机票,税后价每人332加币,10月4日出发,8日返程,机票过了一星期后寄到了家里。
接下去就是制定旅游线路以及租车和住宿问题。租车非常简单,到几个大的租车行的网站,如Herts、National、Budget、Thrifty等,输入租车和还车的具体时间地点,以及车型。比较了价格后,我在Budget订了Nissan 的Altima,每天租金19美金(不包括保险),不限公里数,而且可以由两人轮流驾驶。
制定线路和住宿就有许多不确定因素,我们计划抵达洛杉矶后就直奔拉斯维加斯,在那儿呆一晚,第二天一早就去大峡谷,但大峡谷究竟要玩几天心里一点儿也没谱,是否能回程时去圣地亚哥野生动物园玩也是未知数,所以我只能按是否去圣地亚哥制定了两套路线,到Mapquest网站上先把两套驾车路线图打印出来。制定好路线后,又到网上比较了几家旅馆,如Motel6、DaysInn、Travelodge等的价钱,把第一天拉斯维加斯和最后一天洛杉矶的酒店订好,这样提前订的好处是可以拿到最好的折扣。
在剩下的几天时间里,我把打算去的一些景点好好研究了一遍。一切准备就绪,只等LG回来后我们就要开始激动人心的旅行了。
美国旅游DIY(上路篇)
LG于10月3日深夜出差回到了家,飞机是4日早晨8点钟的,911后的规定是提前3小时到达机场。尽管LG已经精疲力尽,没办法,我们还是得打电话预约早晨5点的出租车赶往机场,还好我们家离机场只有15分钟的车程。
五点多钟我们赶到机场Check-in,托运了一件行李后,就去入关处等候,这么早已经有很多人在排队。从温哥华国际机场飞往美国方向的,美国入境海关设在温哥华机场(听起来很奇怪吧?我觉得多半是美国人仗势欺人,要不怎么没听说加拿大有把入境海关设在美国的。)好不容易排到了入境处官员的面前,问了我们几个简单的问题如去美国干什么,呆多少天,就进了关(这就算进美国了,可我人还在温哥华呢!),前后也就花了一个多小时,可能是比较早的缘故吧。离飞机起飞还有一个多小时,我们在机场内的Burger King吃了早餐,就等在了加航登机口附近。
飞机准时起飞,从温哥华到洛杉矶需飞行近三个小时,加航提供了早餐,我要了带水果的。用完早餐没多久就抵达了目的地——洛杉矶国际机场。我们拿了行李就走出了机场,阳光明媚,不用上班啦,我们的心情格外轻松愉快。
出了机场第一件事是要去取车,机场内的Budget租车的柜台连个人影都没有,只有块指示牌让在机场出租车的地方等Budget的班车。我们等在车站时发现各大出租车行的班车每隔几分钟就来一辆接人,而且大多都是大巴,看来这地方租车的人奇多。我们乘上了Budget的班车,在机场附近的第一站下了车,哇!好大一个租车公司,几百辆各种款式的车子停在那儿,所有进出的车辆都要经过一道有四个口的关卡,班车放下我们后继续送人到其它Budget取车点。
到了取车的柜台,又有十几个人在排队,我们凭着网上打印下来的预订单,出示了两人的加拿大驾照和信用卡,付了钱又买了保险就算好了。因为预订的Nissan Altima还没还回来,就免费升级到了Ford Tauraus(FullSize)。工作人员给了一个停车场车位的号码,让我们自己去找这个停车的位置,车钥匙都在车内。按着号码找到了车,拿着车内的钥匙发动起来,我们就准备开出去。到了出口处的关卡,工作人员又拿着我们租车的凭证仔细核对了车型,这才放行。我这时才恍然大悟,怪不得车钥匙就随便的放在车上,车门都是开着的,如果你拿错了车也不用担心,出口处查的严着呢!我们不得不佩服租车公司的管理有方。
这里我还想罗嗦的是关于租车保险的事,这可是有很大的学问。如果你在租车过程中未发生任何事那当然万事大吉,但如果出了事,买的保险又不当的话,可是会损失惨重的!我这绝不是危言耸听,我们就有一位在温哥华的朋友在租车时未仔细阅读保险条款(他只租了一天),结果撞车后才发现买的碰撞险是自己支付低于 2500加币部分的费用,保险公司支付高于2500加币部分的费用。他撞的车修了近3000加币,自己出了2500加币,可想而之有多倒霉。有了前车之鉴,我们租车时特意买了最全的保险,每天30多美元,除了必须买的第三方责任险,碰撞/丢失险,还包括免费拖车,行李保险等。出了任何事情自己都无需承担任何费用。当然这里有许多信用卡的金卡和白金卡在租车时可以自动免费承担碰撞/丢失险,但我们总觉得这种信用卡的保险在申报起来可能会很麻烦,万一出了事故还要首先和信用卡的保险公司取得联系,再和租车公司交涉,一定会费时费力,所以从未试过,也就不能提供这方面的经验。
LG开着租来的 Ford车,过了几个路口,按着mapquest的指示,一个转弯上了高速公路。哇塞,洛杉矶的高速公路可真吓人,密密麻麻的车辆在四五车道的公路上以时数140公里的速度一辆紧跟一辆的行驶,这要在温哥华让ICBC看到了,可不全都违反了保持2秒车距的规定。LG紧握方向盘,注意力高度集中,完全忘记了连日在外出差的疲劳,向我们第一个目的地——拉斯维加斯驶去。
页面 2 / 4
美国旅游DIY(旅途篇一:拉斯维加斯)
出了洛杉矶便驶上了州际15号公路,沿这条公路一直开就能到拉斯维加斯,洛杉矶到拉斯维加斯约300英里,开车约四个多小时。我们在沿途的一个重要的交通枢钮城市Barstow稍做歇息。 Barstow位于15号公路和40号公路的交汇点,那里有一家非常有名的名牌服饰直销广场。我们在广场内一家叫Panda Express的连锁中式快餐店吃了午饭(这时已经下午两点多钟了),两菜加炒面或炒饭的套餐约5美元,每人还给一个Fortune Cookie,里面会有一张纸条写着你的运势。用完饭我们到广场里逛了一圈,那里有Levis、Tommy、Guess、Polo、Esprit、 Timberland等各大品牌的服饰,价格比我们平时在商店里买的稍便宜些,在广场问讯处还可以免费拿一本折扣券,有些品牌拿折扣券会更便宜些。逛了约一个小时,LG催促我继续上路,我们要天黑之前到拉斯维加斯,以便有充足的时间欣赏其绚丽多彩的夜景。我只好恋恋不舍的离开了Barstow。
回到15号公路,LG加足了马力向目的地开去,沿途都是一望无际的Mojave沙漠。开了约两个小时,就发现路的两边开始稀稀拉拉的出现一些很有特色的建筑物,大多是连着赌场的小型酒店,又开了一段路,眼前豁然开朗,“海市蜃楼!”我好象Kevin Costner主演的电影《未来水世界》里人们在汪洋大海中发现绿洲般地激动。只见远处无数造型各异的霓虹灯在夜幕降临之际发出诱人的色彩,吸引着你一步一步的融入它醉人的怀抱。公路也一下子变宽,车流不断的从四面八方涌入这座沙漠中的城市,每个人好象都迫不及待的想赶去属于他的那个地方。
进城后首先得找到预订的旅馆,按着mapquest的指示,我们没费什么力气就找到了DaysInn,与那些著名酒店比起来,我们的旅馆显得十分寒酸,好在房间里设施干净齐全,泊车又不收费,在目前的季节住一晚也只要30美元,还是觉得物有所值。
在旅馆里稍微休息了一会儿,我们就走出了门,外面的空气有点闷热,不过还能透过气来。一个转弯就是拉斯维加斯观光大道,所有大型酒店赌场都集中在道路的两边,我们的位置是在这条大道的最北端。首先映入眼帘的是马路对面象海洋世界一样的酒店,酒店的下面是一些商场和赌场。继续往前走了一个街区,感觉酒店集中的地方离的很远,于是走回酒店上了我们的Taurus向着那片灯光开去。开了十几个街区,发现马路两边的人开始增多,一些著名的酒店如Circus Circus,Stardust相继出现,经过一家叫New Frontier的酒店时,我突然发现Panda Express的招牌,嘿,正愁没地方吃晚饭呢,这就让我撞上了,我们于是在停车场泊好车,准备去饱餐一顿。到了酒店门口,有一对金童玉女在那儿发什么东西,我正想往里面冲,玉女比我还猴急的拦住我:“你是中国人吗?”一听我说是,她马上给了我们一人一张券,还解释说可以凭券在酒店的赌场内免费玩一次某种赌博机。看来中国人好赌已经闻名天下了,哀哉哀哉!拿着那两张券我们走进酒店,整个酒店的大堂就是一个大型赌场,不过赌的人好象并不多,不知是不是911 后旅游业黯淡的显示。在赌场的一角我们找到了Panda Express,晚饭后我琢磨着如何用掉这两张券,就拉着LG到那赌博机前,一人拉一下机器上的操纵杆,没戏,走人,这就把两张券花了,一点也不好玩。
走出了New Frontier,我们沿着观光大道前行,人越来越多,在Treasure Island酒店前终于挤得个水泄不通,仔细听去,没几个人在说英语,大多都是来自世界各国的观光客酒店前有海盗船表演,只见一名穿着中世纪服装的"海盗 "驾着一艘小木船往来于两艘居大的帆船之间,幽暗的灯光、雾光交织在一起,让人有大难临头的紧迫感,配着招牌上的骷蝼,说不出的诡秘。
随着人流缓缓的往前走来到了Mirage酒店,该酒店以每隔半小时左右的火山表演著称,好象是前一场表演刚结束,酒店前冷冷清清,我们留了个影,决定先往前走,回头再来看火山表演。
Mirage 前面是富丽堂皇的凯撒宫——集购物和娱乐为一体的巨型酒店赌场,整个酒店承袭了古罗马时代的建筑风格,入口处火把映照下的骏马格外英武进入凯撒宫,人恍若走进了仙境古罗马神话中人物的雕像,房顶上蓝天白云和神话故事的彩绘,传说中的特洛伊木马,还有绕梁一圈的热带鱼,让我流连忘返。酒店里一间一间的名牌服饰店对我完全失去了吸引力,我只想再多看一眼那些充满艺术气息的景物。
出了凯撒宫,忽然觉得有一丝倦意,街上的霓虹灯不再让我感到惊异,取而代之的是旅途的疲劳。奢侈腐华的夜生活也渐渐向我们露出他狰狞的嘴脸,我仿佛看见他对我们说:“嘿,这里只属于那些纸醉金迷、纵情享乐的人们,你们还是滚回去吧!”我和先生顺着原路往回去停车的地方,已经十点多了,街上的人却越来越多,不时有人在发放应召女郎的广告册,册子上的女郎个个都是美丽绝伦,风情万种。
顺着原路走,Mirage酒店前聚满了人,马上就要火山表演了。我和LG赶紧抢占了有利地形,一会儿就听见地动山摇的巨响,火焰慢慢的从火山口冲出,然后是擎天飞柱的一道火光照亮了整个水池,水池中也燃起了无数小的火焰,配上波浪的声音,十分壮观。
看完火山表演,找到了停车的地方,上车后LG提议我们开着车沿着观光大道兜一圈,于是我看见了Bellagio酒店前面长长的音乐喷泉,MGM酒店前威武的狮身人面像,阿拉丁酒店前的童话世界,BALLY酒店前ShowGirl的灯箱广告。。
回到了旅馆,已经精疲力尽,闭上眼睛,脑海中回荡的还是那些梦幻般的景象,只觉得头脑发胀。唉,拉斯维加斯,我不属于你!
美国旅游DIY(旅途篇二:大峡谷)
第二天早上一睁开眼睛,我和LG就收拾起行李上了路,开向下一个目的地——大峡谷。在开出拉斯维加斯的时候,我看到了一个小小的教堂,门口的招牌上画着一颗大大的红心,上面写着领取结婚证什么的。我猛然记起曾经在哪本书上看到过,拉斯维加斯有一个非常有名的婚礼教堂,不用出示任何证件就可领结婚证,不过是否具有法律效应就不得而知了。下次我再来拉斯维加斯,一定要去领一张结婚证,想着想着,心里美滋滋的,发了好一会儿呆,直到离开了这座沙漠中的海市蜃楼。
沿着93号公路开,一路上还是漫无边际的沙漠,百般无聊之际,我打开了我的手机, Guess What?居然还有信号!看来Rogers在北美的网络覆盖非常好,在这荒无人烟的地方还能使用真够强劲。开了有一个小时的样子,进入了山区,地形开始险峻起来,公路盘山而建,十分狭窄。仔细一看路牌,原来我们从内华达州驶入了亚里桑那州。才进入不久,就看见前面停着好几辆警车,我们前面的几辆大货车都被拦下检查,我赶紧从背包里拿出我和LG的护照配合他们的工作。轮到我们时,那位女警只朝我们车里瞄了一眼,就向我们一挥手让我们走了。我仔细一琢磨,对了,一定是美国人被恐怖分子吓坏了,看见是辆大货车就怀疑有人装满了炸弹要往哪个楼里撞,一朝被蛇咬,十年怕草绳啊!
继续前行,看到的仍然是一片荒山野岭,很多红色的岩石裸露出风化的断层,和电视杂志上看到的大峡谷非常相似,很有几分壮观,看看mapquest打印出来的路线图,离我们要去的大峡谷国家公园南峰的入口处还有几百公里,我们现在看到的大概仅仅是诺大一片大峡谷区域的边缘部分吧。我期待着看见更为宏伟壮观的大峡谷。
在一个叫Kingman的小镇上,我们下了高速公路,在那里的Burger King用了早午餐,这时已经十点多钟,按着mapquest的指示,从拉斯维加斯到大峡谷要近七个小时,不过LG一路上一直开快车(其实他也不累,把定速巡航一开,只要眼睛看着前方随时准备刹车就行了),我估计全程只需五个小时就够了。稍微休息了片刻,在Kingman转上了40号公路,这也是一条非常繁忙的公路,很多大货车穿梭其中,时速都在120公里以上。车行一个多小时,在Williams镇,我们又转到了通向大峡谷的64号公路,距大峡谷国家公园还有不到一百公里,虽然公路上的车辆并不多,但由于是单车道,超车比较困难,有几辆开得较慢的车横在路中间你也没办法,找个机会超过了这辆,马上又会出现另一辆害群之马。这样一直开到公园门口,也用了一个多小时。
大峡谷国家公园门口有个收费处,连人带车收费20美元,可以玩7天,公园内的观光车免费搭乘(有些路线私人车辆禁止进入,只能乘园内的观光车),北美旅游确实便宜。顺着车流往里开,在一个观光台的周围停了好多车辆,我对LG说:“我们先往里开开,找个人少的地方泊完车研究一下这里的景点再游览吧。”才说完,我立刻发现从观光台的缝隙处往下看是一片非常开阔的峡谷地带,那一刻的诧异美的无法用语言来形容。于是我们不管三七二十一,顺着路边停了车。才下了车我就啪嗒一声摔倒在沙地上,原来是我穿的凉鞋太滑的缘故,想起刚才车上我还正和LG讨论两轮驱动和四轮驱动的原理,看着LG穿的登山鞋,我不禁苦笑着说:“你瞧我这两轮驱动,到了山路上就打滑,哪及得上你的四轮驱动。”LG哈哈大笑的把我从地上拉了起来。
登上了观光台,放眼望去,那些延绵起伏、宏伟壮观的岩层山脉,被科罗拉多河经过几百万年的冲洗分为北峰和南峰两部分。这些岩石上几乎寸草不生,在烈日的照射下泛出耀眼的红色,你好象能够感觉到它坚韧不拔的个性,我不禁感叹起造物主的神奇。
在观光台上停留了许久,我们开着车进入园内的酒店区,想先把今晚的酒店订好再说,可是问了好几家相对比较便宜的酒店,都已经人满为患了。我和LG 垂头丧气地回到了车上,“算了,我们先去玩吧,不行晚上开出公园找旅馆呗,再不行可以睡在车上,反正我们是来玩的嘛!”LG安慰起我来。于是我重新振作起精神,拿出入口处发的导游图。我们停好车,按着导游图上的指示来到乘观光车的站台上,园内的观光车分为三条线路,西线、东线和连接东西线的中间一条线路,其中西线禁止私人车辆进入。我们首先上了西线的观光车顺着南峰往西开,乘客在每个风景点都可以自由上下,下车的乘客再乘坐下一班车继续观光,非常方便,我们在最后一站Hermits Rest留了影乘着车回到了起点站。从导游图上看,东线是看科罗拉多河最好的一条线路,我们开着车一直往东开,在GrandView Point和Moran Point停下车,果然科罗拉多河在峡谷谷底象一条长长的蛇扭摆着它的躯体,若隐若现,我无法想象就是这条从高处看来细细窄窄的河居然能把大峡谷一劈为二,几百万年前它一定又是另一番景象吧!
顺着东线一直开我们开上了沙漠观光路,据导游图上的介绍,最东面可以看到远处的沙漠。可是等我们开到了沙漠观光点时,已经快五点多钟了,瞭望塔结束了参观时间,正好把我们拦在了下面。我们无缘见到那一片沙漠了。附近的加油站也已经关门,车上的油快用完了,我查了一下地图,最近的加油站在公园南侧出了收费口的地方,也有好几十公里,我们别无选择,只能冒险往回开,希望在油用完前找到加油站。回去的路上,看到了远处树林里一道强烈的红光,而且越来越红,越来越亮,是日落!我忽然记起在中线和西线的几个点可以看到日落,可是我们似乎离的太远,只能从密林中窥探它的美伦美奂。
从原路开出了公园,在64号公路上我们找到了加油站,Taurus“油”足饭饱了,可我们距离上午在 Kingman的早午餐已经有快十个小时了,晚上住哪里还没有个着落,64号公路上黑漆漆的,连个路灯都没有,伸手不见五指。所幸前面距离加油站不远的地方有很多酒店,Holiday Inn, Best Western, Comfort Inn等,应有尽有。我们去一打听,价钱不算太便宜,而且得到的答案都是只剩最后一间,没有任何折扣。赶情他们都是和公园里的酒店串通好的,知道那里已经客满了,你不住也得住了,不过想想其实价格还是比公园内的酒店便宜些,我们只好又回到了Best Western,在那位幸灾乐祸的服务员面前要了一间房。拿着钥匙一走进房间,我的心情一下子又愉快了起来,酒店设施一流,三星级的酒店能赶上北京上海的五星级,房间布置的温馨典雅,看来这七十多美元还花得真值得。行李一放下,我们在附近找了一家Pizza Hut,买了一个Pizza外加一打鸡翅膀,回到酒店狼吞虎咽地吃了个精光。
晚上美美地睡了一觉,睡梦中我仿佛见到了大峡谷中那一轮火红火红的落日。
美国旅游DIY(旅途篇三:圣地亚哥野生动物园)
六日早晨九点多钟,我们退了房,还是老规矩,先开车上路,等肚子饿了再找地方吃早餐。其实在北美的高速公路上,每隔几个出口就会老远看见加油站、快餐店和旅馆的招牌,随时可以下去打个牙祭,稍事休整,非常方便。
今天的任务是从大峡谷一直开到圣地亚哥附近,准备明天一早去游览圣地亚哥野生动物园。这两地相距800多公里,我们先沿着64号公路一直开到 Williams镇,然后转40号公路,进入加利福尼亚后一路上都是Mojave沙漠。Mojave沙漠位于加利福尼亚州的东南面,与内华达、亚利桑那和尤他州交界,占地25,000平方英里,沙漠上种满了矮矮的灌木林,我想是防止沙化加剧的原因吧,要知道洛杉矶、旧金山等人口密集的大城市都在距 Mojave沙漠仅几百公里的地方,一旦沙漠面积扩大,后果会不堪设想。常有报导说中国西北的沙漠地带正以惊人的速度吞没农田,北京每年的沙尘暴现象日趋严重。国家由于资金短缺,只在沙漠的四周种植防护林,收效甚微,因为大面积未种植防护林的沙漠会很快席卷而来,迅速把防护林湮没。我觉得我国只有象这样将整个沙漠综合治理,才能造福子孙后代,否则正会象朱镕基总理所说的那样,“北京沙尘暴再严重下去,要考虑迁都了。”
http://travel.westca.com/content/view/1031/76/
今年十月我和LG决定在他生日的时候乘飞机去美国洛杉矶,然后租车去大峡谷和拉斯维加斯游览。由于LG在启程之前一直出差在外,我只能负起了行程总策划的职责。
首先是订机票,经过反复比较,又因为我们有加航的里程积分卡,我在加航网上订了两人来回洛杉矶的机票,税后价每人332加币,10月4日出发,8日返程,机票过了一星期后寄到了家里。
接下去就是制定旅游线路以及租车和住宿问题。租车非常简单,到几个大的租车行的网站,如Herts、National、Budget、Thrifty等,输入租车和还车的具体时间地点,以及车型。比较了价格后,我在Budget订了Nissan 的Altima,每天租金19美金(不包括保险),不限公里数,而且可以由两人轮流驾驶。
制定线路和住宿就有许多不确定因素,我们计划抵达洛杉矶后就直奔拉斯维加斯,在那儿呆一晚,第二天一早就去大峡谷,但大峡谷究竟要玩几天心里一点儿也没谱,是否能回程时去圣地亚哥野生动物园玩也是未知数,所以我只能按是否去圣地亚哥制定了两套路线,到Mapquest网站上先把两套驾车路线图打印出来。制定好路线后,又到网上比较了几家旅馆,如Motel6、DaysInn、Travelodge等的价钱,把第一天拉斯维加斯和最后一天洛杉矶的酒店订好,这样提前订的好处是可以拿到最好的折扣。
在剩下的几天时间里,我把打算去的一些景点好好研究了一遍。一切准备就绪,只等LG回来后我们就要开始激动人心的旅行了。
美国旅游DIY(上路篇)
LG于10月3日深夜出差回到了家,飞机是4日早晨8点钟的,911后的规定是提前3小时到达机场。尽管LG已经精疲力尽,没办法,我们还是得打电话预约早晨5点的出租车赶往机场,还好我们家离机场只有15分钟的车程。
五点多钟我们赶到机场Check-in,托运了一件行李后,就去入关处等候,这么早已经有很多人在排队。从温哥华国际机场飞往美国方向的,美国入境海关设在温哥华机场(听起来很奇怪吧?我觉得多半是美国人仗势欺人,要不怎么没听说加拿大有把入境海关设在美国的。)好不容易排到了入境处官员的面前,问了我们几个简单的问题如去美国干什么,呆多少天,就进了关(这就算进美国了,可我人还在温哥华呢!),前后也就花了一个多小时,可能是比较早的缘故吧。离飞机起飞还有一个多小时,我们在机场内的Burger King吃了早餐,就等在了加航登机口附近。
飞机准时起飞,从温哥华到洛杉矶需飞行近三个小时,加航提供了早餐,我要了带水果的。用完早餐没多久就抵达了目的地——洛杉矶国际机场。我们拿了行李就走出了机场,阳光明媚,不用上班啦,我们的心情格外轻松愉快。
出了机场第一件事是要去取车,机场内的Budget租车的柜台连个人影都没有,只有块指示牌让在机场出租车的地方等Budget的班车。我们等在车站时发现各大出租车行的班车每隔几分钟就来一辆接人,而且大多都是大巴,看来这地方租车的人奇多。我们乘上了Budget的班车,在机场附近的第一站下了车,哇!好大一个租车公司,几百辆各种款式的车子停在那儿,所有进出的车辆都要经过一道有四个口的关卡,班车放下我们后继续送人到其它Budget取车点。
到了取车的柜台,又有十几个人在排队,我们凭着网上打印下来的预订单,出示了两人的加拿大驾照和信用卡,付了钱又买了保险就算好了。因为预订的Nissan Altima还没还回来,就免费升级到了Ford Tauraus(FullSize)。工作人员给了一个停车场车位的号码,让我们自己去找这个停车的位置,车钥匙都在车内。按着号码找到了车,拿着车内的钥匙发动起来,我们就准备开出去。到了出口处的关卡,工作人员又拿着我们租车的凭证仔细核对了车型,这才放行。我这时才恍然大悟,怪不得车钥匙就随便的放在车上,车门都是开着的,如果你拿错了车也不用担心,出口处查的严着呢!我们不得不佩服租车公司的管理有方。
这里我还想罗嗦的是关于租车保险的事,这可是有很大的学问。如果你在租车过程中未发生任何事那当然万事大吉,但如果出了事,买的保险又不当的话,可是会损失惨重的!我这绝不是危言耸听,我们就有一位在温哥华的朋友在租车时未仔细阅读保险条款(他只租了一天),结果撞车后才发现买的碰撞险是自己支付低于 2500加币部分的费用,保险公司支付高于2500加币部分的费用。他撞的车修了近3000加币,自己出了2500加币,可想而之有多倒霉。有了前车之鉴,我们租车时特意买了最全的保险,每天30多美元,除了必须买的第三方责任险,碰撞/丢失险,还包括免费拖车,行李保险等。出了任何事情自己都无需承担任何费用。当然这里有许多信用卡的金卡和白金卡在租车时可以自动免费承担碰撞/丢失险,但我们总觉得这种信用卡的保险在申报起来可能会很麻烦,万一出了事故还要首先和信用卡的保险公司取得联系,再和租车公司交涉,一定会费时费力,所以从未试过,也就不能提供这方面的经验。
LG开着租来的 Ford车,过了几个路口,按着mapquest的指示,一个转弯上了高速公路。哇塞,洛杉矶的高速公路可真吓人,密密麻麻的车辆在四五车道的公路上以时数140公里的速度一辆紧跟一辆的行驶,这要在温哥华让ICBC看到了,可不全都违反了保持2秒车距的规定。LG紧握方向盘,注意力高度集中,完全忘记了连日在外出差的疲劳,向我们第一个目的地——拉斯维加斯驶去。
页面 2 / 4
美国旅游DIY(旅途篇一:拉斯维加斯)
出了洛杉矶便驶上了州际15号公路,沿这条公路一直开就能到拉斯维加斯,洛杉矶到拉斯维加斯约300英里,开车约四个多小时。我们在沿途的一个重要的交通枢钮城市Barstow稍做歇息。 Barstow位于15号公路和40号公路的交汇点,那里有一家非常有名的名牌服饰直销广场。我们在广场内一家叫Panda Express的连锁中式快餐店吃了午饭(这时已经下午两点多钟了),两菜加炒面或炒饭的套餐约5美元,每人还给一个Fortune Cookie,里面会有一张纸条写着你的运势。用完饭我们到广场里逛了一圈,那里有Levis、Tommy、Guess、Polo、Esprit、 Timberland等各大品牌的服饰,价格比我们平时在商店里买的稍便宜些,在广场问讯处还可以免费拿一本折扣券,有些品牌拿折扣券会更便宜些。逛了约一个小时,LG催促我继续上路,我们要天黑之前到拉斯维加斯,以便有充足的时间欣赏其绚丽多彩的夜景。我只好恋恋不舍的离开了Barstow。
回到15号公路,LG加足了马力向目的地开去,沿途都是一望无际的Mojave沙漠。开了约两个小时,就发现路的两边开始稀稀拉拉的出现一些很有特色的建筑物,大多是连着赌场的小型酒店,又开了一段路,眼前豁然开朗,“海市蜃楼!”我好象Kevin Costner主演的电影《未来水世界》里人们在汪洋大海中发现绿洲般地激动。只见远处无数造型各异的霓虹灯在夜幕降临之际发出诱人的色彩,吸引着你一步一步的融入它醉人的怀抱。公路也一下子变宽,车流不断的从四面八方涌入这座沙漠中的城市,每个人好象都迫不及待的想赶去属于他的那个地方。
进城后首先得找到预订的旅馆,按着mapquest的指示,我们没费什么力气就找到了DaysInn,与那些著名酒店比起来,我们的旅馆显得十分寒酸,好在房间里设施干净齐全,泊车又不收费,在目前的季节住一晚也只要30美元,还是觉得物有所值。
在旅馆里稍微休息了一会儿,我们就走出了门,外面的空气有点闷热,不过还能透过气来。一个转弯就是拉斯维加斯观光大道,所有大型酒店赌场都集中在道路的两边,我们的位置是在这条大道的最北端。首先映入眼帘的是马路对面象海洋世界一样的酒店,酒店的下面是一些商场和赌场。继续往前走了一个街区,感觉酒店集中的地方离的很远,于是走回酒店上了我们的Taurus向着那片灯光开去。开了十几个街区,发现马路两边的人开始增多,一些著名的酒店如Circus Circus,Stardust相继出现,经过一家叫New Frontier的酒店时,我突然发现Panda Express的招牌,嘿,正愁没地方吃晚饭呢,这就让我撞上了,我们于是在停车场泊好车,准备去饱餐一顿。到了酒店门口,有一对金童玉女在那儿发什么东西,我正想往里面冲,玉女比我还猴急的拦住我:“你是中国人吗?”一听我说是,她马上给了我们一人一张券,还解释说可以凭券在酒店的赌场内免费玩一次某种赌博机。看来中国人好赌已经闻名天下了,哀哉哀哉!拿着那两张券我们走进酒店,整个酒店的大堂就是一个大型赌场,不过赌的人好象并不多,不知是不是911 后旅游业黯淡的显示。在赌场的一角我们找到了Panda Express,晚饭后我琢磨着如何用掉这两张券,就拉着LG到那赌博机前,一人拉一下机器上的操纵杆,没戏,走人,这就把两张券花了,一点也不好玩。
走出了New Frontier,我们沿着观光大道前行,人越来越多,在Treasure Island酒店前终于挤得个水泄不通,仔细听去,没几个人在说英语,大多都是来自世界各国的观光客酒店前有海盗船表演,只见一名穿着中世纪服装的"海盗 "驾着一艘小木船往来于两艘居大的帆船之间,幽暗的灯光、雾光交织在一起,让人有大难临头的紧迫感,配着招牌上的骷蝼,说不出的诡秘。
随着人流缓缓的往前走来到了Mirage酒店,该酒店以每隔半小时左右的火山表演著称,好象是前一场表演刚结束,酒店前冷冷清清,我们留了个影,决定先往前走,回头再来看火山表演。
Mirage 前面是富丽堂皇的凯撒宫——集购物和娱乐为一体的巨型酒店赌场,整个酒店承袭了古罗马时代的建筑风格,入口处火把映照下的骏马格外英武进入凯撒宫,人恍若走进了仙境古罗马神话中人物的雕像,房顶上蓝天白云和神话故事的彩绘,传说中的特洛伊木马,还有绕梁一圈的热带鱼,让我流连忘返。酒店里一间一间的名牌服饰店对我完全失去了吸引力,我只想再多看一眼那些充满艺术气息的景物。
出了凯撒宫,忽然觉得有一丝倦意,街上的霓虹灯不再让我感到惊异,取而代之的是旅途的疲劳。奢侈腐华的夜生活也渐渐向我们露出他狰狞的嘴脸,我仿佛看见他对我们说:“嘿,这里只属于那些纸醉金迷、纵情享乐的人们,你们还是滚回去吧!”我和先生顺着原路往回去停车的地方,已经十点多了,街上的人却越来越多,不时有人在发放应召女郎的广告册,册子上的女郎个个都是美丽绝伦,风情万种。
顺着原路走,Mirage酒店前聚满了人,马上就要火山表演了。我和LG赶紧抢占了有利地形,一会儿就听见地动山摇的巨响,火焰慢慢的从火山口冲出,然后是擎天飞柱的一道火光照亮了整个水池,水池中也燃起了无数小的火焰,配上波浪的声音,十分壮观。
看完火山表演,找到了停车的地方,上车后LG提议我们开着车沿着观光大道兜一圈,于是我看见了Bellagio酒店前面长长的音乐喷泉,MGM酒店前威武的狮身人面像,阿拉丁酒店前的童话世界,BALLY酒店前ShowGirl的灯箱广告。。
回到了旅馆,已经精疲力尽,闭上眼睛,脑海中回荡的还是那些梦幻般的景象,只觉得头脑发胀。唉,拉斯维加斯,我不属于你!
美国旅游DIY(旅途篇二:大峡谷)
第二天早上一睁开眼睛,我和LG就收拾起行李上了路,开向下一个目的地——大峡谷。在开出拉斯维加斯的时候,我看到了一个小小的教堂,门口的招牌上画着一颗大大的红心,上面写着领取结婚证什么的。我猛然记起曾经在哪本书上看到过,拉斯维加斯有一个非常有名的婚礼教堂,不用出示任何证件就可领结婚证,不过是否具有法律效应就不得而知了。下次我再来拉斯维加斯,一定要去领一张结婚证,想着想着,心里美滋滋的,发了好一会儿呆,直到离开了这座沙漠中的海市蜃楼。
沿着93号公路开,一路上还是漫无边际的沙漠,百般无聊之际,我打开了我的手机, Guess What?居然还有信号!看来Rogers在北美的网络覆盖非常好,在这荒无人烟的地方还能使用真够强劲。开了有一个小时的样子,进入了山区,地形开始险峻起来,公路盘山而建,十分狭窄。仔细一看路牌,原来我们从内华达州驶入了亚里桑那州。才进入不久,就看见前面停着好几辆警车,我们前面的几辆大货车都被拦下检查,我赶紧从背包里拿出我和LG的护照配合他们的工作。轮到我们时,那位女警只朝我们车里瞄了一眼,就向我们一挥手让我们走了。我仔细一琢磨,对了,一定是美国人被恐怖分子吓坏了,看见是辆大货车就怀疑有人装满了炸弹要往哪个楼里撞,一朝被蛇咬,十年怕草绳啊!
继续前行,看到的仍然是一片荒山野岭,很多红色的岩石裸露出风化的断层,和电视杂志上看到的大峡谷非常相似,很有几分壮观,看看mapquest打印出来的路线图,离我们要去的大峡谷国家公园南峰的入口处还有几百公里,我们现在看到的大概仅仅是诺大一片大峡谷区域的边缘部分吧。我期待着看见更为宏伟壮观的大峡谷。
在一个叫Kingman的小镇上,我们下了高速公路,在那里的Burger King用了早午餐,这时已经十点多钟,按着mapquest的指示,从拉斯维加斯到大峡谷要近七个小时,不过LG一路上一直开快车(其实他也不累,把定速巡航一开,只要眼睛看着前方随时准备刹车就行了),我估计全程只需五个小时就够了。稍微休息了片刻,在Kingman转上了40号公路,这也是一条非常繁忙的公路,很多大货车穿梭其中,时速都在120公里以上。车行一个多小时,在Williams镇,我们又转到了通向大峡谷的64号公路,距大峡谷国家公园还有不到一百公里,虽然公路上的车辆并不多,但由于是单车道,超车比较困难,有几辆开得较慢的车横在路中间你也没办法,找个机会超过了这辆,马上又会出现另一辆害群之马。这样一直开到公园门口,也用了一个多小时。
大峡谷国家公园门口有个收费处,连人带车收费20美元,可以玩7天,公园内的观光车免费搭乘(有些路线私人车辆禁止进入,只能乘园内的观光车),北美旅游确实便宜。顺着车流往里开,在一个观光台的周围停了好多车辆,我对LG说:“我们先往里开开,找个人少的地方泊完车研究一下这里的景点再游览吧。”才说完,我立刻发现从观光台的缝隙处往下看是一片非常开阔的峡谷地带,那一刻的诧异美的无法用语言来形容。于是我们不管三七二十一,顺着路边停了车。才下了车我就啪嗒一声摔倒在沙地上,原来是我穿的凉鞋太滑的缘故,想起刚才车上我还正和LG讨论两轮驱动和四轮驱动的原理,看着LG穿的登山鞋,我不禁苦笑着说:“你瞧我这两轮驱动,到了山路上就打滑,哪及得上你的四轮驱动。”LG哈哈大笑的把我从地上拉了起来。
登上了观光台,放眼望去,那些延绵起伏、宏伟壮观的岩层山脉,被科罗拉多河经过几百万年的冲洗分为北峰和南峰两部分。这些岩石上几乎寸草不生,在烈日的照射下泛出耀眼的红色,你好象能够感觉到它坚韧不拔的个性,我不禁感叹起造物主的神奇。
在观光台上停留了许久,我们开着车进入园内的酒店区,想先把今晚的酒店订好再说,可是问了好几家相对比较便宜的酒店,都已经人满为患了。我和LG 垂头丧气地回到了车上,“算了,我们先去玩吧,不行晚上开出公园找旅馆呗,再不行可以睡在车上,反正我们是来玩的嘛!”LG安慰起我来。于是我重新振作起精神,拿出入口处发的导游图。我们停好车,按着导游图上的指示来到乘观光车的站台上,园内的观光车分为三条线路,西线、东线和连接东西线的中间一条线路,其中西线禁止私人车辆进入。我们首先上了西线的观光车顺着南峰往西开,乘客在每个风景点都可以自由上下,下车的乘客再乘坐下一班车继续观光,非常方便,我们在最后一站Hermits Rest留了影乘着车回到了起点站。从导游图上看,东线是看科罗拉多河最好的一条线路,我们开着车一直往东开,在GrandView Point和Moran Point停下车,果然科罗拉多河在峡谷谷底象一条长长的蛇扭摆着它的躯体,若隐若现,我无法想象就是这条从高处看来细细窄窄的河居然能把大峡谷一劈为二,几百万年前它一定又是另一番景象吧!
顺着东线一直开我们开上了沙漠观光路,据导游图上的介绍,最东面可以看到远处的沙漠。可是等我们开到了沙漠观光点时,已经快五点多钟了,瞭望塔结束了参观时间,正好把我们拦在了下面。我们无缘见到那一片沙漠了。附近的加油站也已经关门,车上的油快用完了,我查了一下地图,最近的加油站在公园南侧出了收费口的地方,也有好几十公里,我们别无选择,只能冒险往回开,希望在油用完前找到加油站。回去的路上,看到了远处树林里一道强烈的红光,而且越来越红,越来越亮,是日落!我忽然记起在中线和西线的几个点可以看到日落,可是我们似乎离的太远,只能从密林中窥探它的美伦美奂。
从原路开出了公园,在64号公路上我们找到了加油站,Taurus“油”足饭饱了,可我们距离上午在 Kingman的早午餐已经有快十个小时了,晚上住哪里还没有个着落,64号公路上黑漆漆的,连个路灯都没有,伸手不见五指。所幸前面距离加油站不远的地方有很多酒店,Holiday Inn, Best Western, Comfort Inn等,应有尽有。我们去一打听,价钱不算太便宜,而且得到的答案都是只剩最后一间,没有任何折扣。赶情他们都是和公园里的酒店串通好的,知道那里已经客满了,你不住也得住了,不过想想其实价格还是比公园内的酒店便宜些,我们只好又回到了Best Western,在那位幸灾乐祸的服务员面前要了一间房。拿着钥匙一走进房间,我的心情一下子又愉快了起来,酒店设施一流,三星级的酒店能赶上北京上海的五星级,房间布置的温馨典雅,看来这七十多美元还花得真值得。行李一放下,我们在附近找了一家Pizza Hut,买了一个Pizza外加一打鸡翅膀,回到酒店狼吞虎咽地吃了个精光。
晚上美美地睡了一觉,睡梦中我仿佛见到了大峡谷中那一轮火红火红的落日。
美国旅游DIY(旅途篇三:圣地亚哥野生动物园)
六日早晨九点多钟,我们退了房,还是老规矩,先开车上路,等肚子饿了再找地方吃早餐。其实在北美的高速公路上,每隔几个出口就会老远看见加油站、快餐店和旅馆的招牌,随时可以下去打个牙祭,稍事休整,非常方便。
今天的任务是从大峡谷一直开到圣地亚哥附近,准备明天一早去游览圣地亚哥野生动物园。这两地相距800多公里,我们先沿着64号公路一直开到 Williams镇,然后转40号公路,进入加利福尼亚后一路上都是Mojave沙漠。Mojave沙漠位于加利福尼亚州的东南面,与内华达、亚利桑那和尤他州交界,占地25,000平方英里,沙漠上种满了矮矮的灌木林,我想是防止沙化加剧的原因吧,要知道洛杉矶、旧金山等人口密集的大城市都在距 Mojave沙漠仅几百公里的地方,一旦沙漠面积扩大,后果会不堪设想。常有报导说中国西北的沙漠地带正以惊人的速度吞没农田,北京每年的沙尘暴现象日趋严重。国家由于资金短缺,只在沙漠的四周种植防护林,收效甚微,因为大面积未种植防护林的沙漠会很快席卷而来,迅速把防护林湮没。我觉得我国只有象这样将整个沙漠综合治理,才能造福子孙后代,否则正会象朱镕基总理所说的那样,“北京沙尘暴再严重下去,要考虑迁都了。”
Friday, August 1, 2008
Howto Config Load profiel on AV/2900
A delay phase at the beginning of a test is often used for allowing the NIC cards to negotiate the links gracefully.
A ramp up phase quickly and proportionally raises the load to the starting level of a capacity assessment test.

A stair stepping phase incrementally adds load to determine the breaking point of the device under test.

A steady phase stress tests the device under test.

The ramp down phase delays conclusion of the test until all of the work-in-progress has completed.

A delay phase at the beginning of a test is often used for allowing the NIC cards to negotiate the links gracefully.
A ramp up phase quickly and proportionally raises the load to the starting level of a capacity assessment test.

A stair stepping phase incrementally adds load to determine the breaking point of the device under test.

A steady phase stress tests the device under test.

The ramp down phase delays conclusion of the test until all of the work-in-progress has completed.

Tuesday, July 22, 2008
Howto read session table
redir, may_dirty
When the session is going through the proxy, it will be marked as redir.
AV scan, content archive and something else will mark the session as redir. IPS won't do that.
The sequence number will be changed if it is proxied.
Ex: Content archive session
root) # d sys session li
session info: proto=6 proto_state=11 expire=3587 timeout=3600 flags=00000000 sockflag=00000000 sockport=0 av_idx=4 use=3
bandwidth=0/sec guaranteed_bandwidth=0/sec traffic=0/sec prio=0 ha_id=0 hakey=0
tunnel=/
state=redir local may_dirty ndr br npu npr
statistic(bytes/packets/err): org=686/12/0 reply=596/8/0 tuples=2
orgin->sink: org pre->post, reply pre->post dev=25->26/26->25 gwy=8.8.103.104/8.8.103.108
hook=pre dir=org act=noop 8.8.103.108:54438->8.8.103.104:21(0.0.0.0:0)
hook=post dir=reply act=noop 8.8.103.104:21->8.8.103.108:54438(0.0.0.0:0)
pos/(before,after) 0/(0,0), 0/(0,0)
misc=20004 policy_id=1 auth_info=0 ids=0x3 vd=4 serial=00001db8 tos=ff/ff app=0
total session 1
Pure IPS session:
# d sys session li
session info: proto=6 proto_state=01 expire=3598 timeout=3600 flags=00000000 sockflag=00000000 sockport=0 av_idx=0 use=3
bandwidth=0/sec guaranteed_bandwidth=0/sec traffic=0/sec prio=0 ha_id=0 hakey=0
tunnel=/
state=ext may_dirty ndr br npu npr
statistic(bytes/packets/err): org=686/12/0 reply=596/8/0 tuples=2
orgin->sink: org pre->post, reply pre->post dev=25->26/26->25 gwy=8.8.103.104/8.8.103.108
hook=pre dir=org act=noop 8.8.103.108:41329->8.8.103.104:21(0.0.0.0:0)
hook=post dir=reply act=noop 8.8.103.104:21->8.8.103.108:41329(0.0.0.0:0)
pos/(before,after) 0/(0,0), 0/(0,0)
misc=20004 policy_id=1 auth_info=0 ids=0x2 vd=4 serial=00001dc2 tos=ff/ff app=0
total session 1
may_dirty and dirty.
Most session which go through the firewall will be marked as may_dirty. This flag means the session is able to be marked as dirty when asymmetric route switch over.
ex: chage the gw of your default route will cause dirty flag show up.
before changing the gw:
FG3K9B3E10700005 # d sys session list
session info: proto=6 proto_state=01 duration=7 expire=3592 timeout=3600 flags=00000000 sockflag=00000000 sockport=0 av_idx=0 use=4
origin-shaper=
reply-shaper=
per_ip_shaper=
ha_id=0 hakey=535
policy_dir=0 tunnel=/
state=may_dirty npu npr rem
statistic(bytes/packets/allow_err): org=164/3/1 reply=132/2/1 tuples=2
orgin->sink: org pre->post, reply pre->post dev=17->18/18->17 gwy=94.1.1.12/93.1.1.11
hook=pre dir=org act=noop 93.1.1.11:51895->94.1.1.12:22(0.0.0.0:0)
hook=post dir=reply act=noop 94.1.1.12:22->93.1.1.11:51895(0.0.0.0:0)
pos/(before,after) 0/(0,0), 0/(0,0)
misc=0 policy_id=2 id_policy_id=0 auth_info=0 chk_client_info=0 vd=0
serial=000011e6 tos=ff/ff app_list=0 app=0
dd_type=0 dd_rule_id=0
per_ip_bandwidth meter: addr=93.1.1.11, bps=0
total session 1
=========================
FG3K9B3E10700005 # d sys session list
session info: proto=6 proto_state=01 duration=1056 expire=3562 timeout=3600 flags=00000000 sockflag=00000000 sockport=0 av_idx=0 use=4
origin-shaper=
reply-shaper=
per_ip_shaper=
ha_id=0 hakey=535
policy_dir=0 tunnel=/
state=dirty may_dirty npu npr rem
statistic(bytes/packets/allow_err): org=164/3/1 reply=132/2/1 tuples=2
orgin->sink: org pre->post, reply pre->post dev=17->0/18->0 gwy=0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0
hook=pre dir=org act=noop 93.1.1.11:51895->94.1.1.12:22(0.0.0.0:0)
hook=post dir=reply act=noop 94.1.1.12:22->93.1.1.11:51895(0.0.0.0:0)
pos/(before,after) 0/(0,0), 0/(0,0)
misc=0 policy_id=2 id_policy_id=0 auth_info=0 chk_client_info=0 vd=0
serial=000011e6 tos=ff/ff app_list=0 app=0
dd_type=0 dd_rule_id=0
per_ip_bandwidth meter: addr=93.1.1.11, bps=0
total session 1
redir, may_dirty
When the session is going through the proxy, it will be marked as redir.
AV scan, content archive and something else will mark the session as redir. IPS won't do that.
The sequence number will be changed if it is proxied.
Ex: Content archive session
root) # d sys session li
session info: proto=6 proto_state=11 expire=3587 timeout=3600 flags=00000000 sockflag=00000000 sockport=0 av_idx=4 use=3
bandwidth=0/sec guaranteed_bandwidth=0/sec traffic=0/sec prio=0 ha_id=0 hakey=0
tunnel=/
state=redir local may_dirty ndr br npu npr
statistic(bytes/packets/err): org=686/12/0 reply=596/8/0 tuples=2
orgin->sink: org pre->post, reply pre->post dev=25->26/26->25 gwy=8.8.103.104/8.8.103.108
hook=pre dir=org act=noop 8.8.103.108:54438->8.8.103.104:21(0.0.0.0:0)
hook=post dir=reply act=noop 8.8.103.104:21->8.8.103.108:54438(0.0.0.0:0)
pos/(before,after) 0/(0,0), 0/(0,0)
misc=20004 policy_id=1 auth_info=0 ids=0x3 vd=4 serial=00001db8 tos=ff/ff app=0
total session 1
Pure IPS session:
# d sys session li
session info: proto=6 proto_state=01 expire=3598 timeout=3600 flags=00000000 sockflag=00000000 sockport=0 av_idx=0 use=3
bandwidth=0/sec guaranteed_bandwidth=0/sec traffic=0/sec prio=0 ha_id=0 hakey=0
tunnel=/
state=ext may_dirty ndr br npu npr
statistic(bytes/packets/err): org=686/12/0 reply=596/8/0 tuples=2
orgin->sink: org pre->post, reply pre->post dev=25->26/26->25 gwy=8.8.103.104/8.8.103.108
hook=pre dir=org act=noop 8.8.103.108:41329->8.8.103.104:21(0.0.0.0:0)
hook=post dir=reply act=noop 8.8.103.104:21->8.8.103.108:41329(0.0.0.0:0)
pos/(before,after) 0/(0,0), 0/(0,0)
misc=20004 policy_id=1 auth_info=0 ids=0x2 vd=4 serial=00001dc2 tos=ff/ff app=0
total session 1
may_dirty and dirty.
Most session which go through the firewall will be marked as may_dirty. This flag means the session is able to be marked as dirty when asymmetric route switch over.
ex: chage the gw of your default route will cause dirty flag show up.
before changing the gw:
FG3K9B3E10700005 # d sys session list
session info: proto=6 proto_state=01 duration=7 expire=3592 timeout=3600 flags=00000000 sockflag=00000000 sockport=0 av_idx=0 use=4
origin-shaper=
reply-shaper=
per_ip_shaper=
ha_id=0 hakey=535
policy_dir=0 tunnel=/
state=may_dirty npu npr rem
statistic(bytes/packets/allow_err): org=164/3/1 reply=132/2/1 tuples=2
orgin->sink: org pre->post, reply pre->post dev=17->18/18->17 gwy=94.1.1.12/93.1.1.11
hook=pre dir=org act=noop 93.1.1.11:51895->94.1.1.12:22(0.0.0.0:0)
hook=post dir=reply act=noop 94.1.1.12:22->93.1.1.11:51895(0.0.0.0:0)
pos/(before,after) 0/(0,0), 0/(0,0)
misc=0 policy_id=2 id_policy_id=0 auth_info=0 chk_client_info=0 vd=0
serial=000011e6 tos=ff/ff app_list=0 app=0
dd_type=0 dd_rule_id=0
per_ip_bandwidth meter: addr=93.1.1.11, bps=0
total session 1
=========================
FG3K9B3E10700005 # d sys session list
session info: proto=6 proto_state=01 duration=1056 expire=3562 timeout=3600 flags=00000000 sockflag=00000000 sockport=0 av_idx=0 use=4
origin-shaper=
reply-shaper=
per_ip_shaper=
ha_id=0 hakey=535
policy_dir=0 tunnel=/
state=dirty may_dirty npu npr rem
statistic(bytes/packets/allow_err): org=164/3/1 reply=132/2/1 tuples=2
orgin->sink: org pre->post, reply pre->post dev=17->0/18->0 gwy=0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0
hook=pre dir=org act=noop 93.1.1.11:51895->94.1.1.12:22(0.0.0.0:0)
hook=post dir=reply act=noop 94.1.1.12:22->93.1.1.11:51895(0.0.0.0:0)
pos/(before,after) 0/(0,0), 0/(0,0)
misc=0 policy_id=2 id_policy_id=0 auth_info=0 chk_client_info=0 vd=0
serial=000011e6 tos=ff/ff app_list=0 app=0
dd_type=0 dd_rule_id=0
per_ip_bandwidth meter: addr=93.1.1.11, bps=0
total session 1
COURSE OBJECTIVES
After completing this course, students will gain competency in the following topics:
Layer 2 Technologies
* PPPoE
* MPLS over ATM
* 802.1Q Tunneling
Interior Gateway Routing
*OSPF
*IS-IS
*Redistribution
*Summarization
*Filtering
*Policy Routing
Exterior Gateway Routing
*IPv4 Unicast BGP
*VPNv4 BGP
*Route Reflection
*Confederation
*Next-Hop Processing
*Redistribution
*Summarization
*Filtering
*Communities
MPLS
*TDP
*LDP
*BGP + Label
*Inter-AS MPLS
*Carrier Supporting Carrier
*Controlling MPLS Label Distribution
*MPLS Traffic Engineering
VPN
*PE-CE Routing with Static Routing
*PE-CE Routing with RIPv2
*PE-CE Routing with OSPF
*PE-CE Routing with EIGRP
*PE-CE Routing with EBGP
*Central Services MPLS VPNs
*MPLS VPNs Extranets
*VRF Import/Export Maps
*BGP Site-Of-Origin
*OSPF Sham-Links
*OSPF Domain-IDs
*Back-to-Back VRF
*Inter-AS MPLS VPNs
*Hierarchical MPLS VPNs
*VRF-Lite
*L2TPv3
IP Multicast
*PIM Dense Mode
*PIM Sparse Mode
*Multicast RPF Failure
*Auto-RP
*PIM NBMA Mode
*Bootstrap Router
*Multicast Source Distribution Protocol (MSDP)
*Anycast RP
*Multicast BGP
*Multicast MPLS VPNs
QoS
*Congestion Management
*Congestion Avoidance
*Shaping
*Policing
*IP Precedence
*DSCP
*MPLS EXP
*QoS Groups
*NBAR
*RSVP
Security
*ACLs
*RPF
*Routing update security
*Common attacks
System Management
*SNMP
*RMON
*Syslog
*NTP
*IP Services
*First Hop Redundancy Protocols
*Netflow
*Accounting
After completing this course, students will gain competency in the following topics:
Layer 2 Technologies
* PPPoE
* MPLS over ATM
* 802.1Q Tunneling
Interior Gateway Routing
*OSPF
*IS-IS
*Redistribution
*Summarization
*Filtering
*Policy Routing
Exterior Gateway Routing
*IPv4 Unicast BGP
*VPNv4 BGP
*Route Reflection
*Confederation
*Next-Hop Processing
*Redistribution
*Summarization
*Filtering
*Communities
MPLS
*TDP
*LDP
*BGP + Label
*Inter-AS MPLS
*Carrier Supporting Carrier
*Controlling MPLS Label Distribution
*MPLS Traffic Engineering
VPN
*PE-CE Routing with Static Routing
*PE-CE Routing with RIPv2
*PE-CE Routing with OSPF
*PE-CE Routing with EIGRP
*PE-CE Routing with EBGP
*Central Services MPLS VPNs
*MPLS VPNs Extranets
*VRF Import/Export Maps
*BGP Site-Of-Origin
*OSPF Sham-Links
*OSPF Domain-IDs
*Back-to-Back VRF
*Inter-AS MPLS VPNs
*Hierarchical MPLS VPNs
*VRF-Lite
*L2TPv3
IP Multicast
*PIM Dense Mode
*PIM Sparse Mode
*Multicast RPF Failure
*Auto-RP
*PIM NBMA Mode
*Bootstrap Router
*Multicast Source Distribution Protocol (MSDP)
*Anycast RP
*Multicast BGP
*Multicast MPLS VPNs
QoS
*Congestion Management
*Congestion Avoidance
*Shaping
*Policing
*IP Precedence
*DSCP
*MPLS EXP
*QoS Groups
*NBAR
*RSVP
Security
*ACLs
*RPF
*Routing update security
*Common attacks
System Management
*SNMP
*RMON
*Syslog
*NTP
*IP Services
*First Hop Redundancy Protocols
*Netflow
*Accounting
Friday, July 18, 2008
Howto capture the traffic on Av/Ref?
1, select the project you wanna do
2, Locate the tag: Run -> Config
3, enable client and server trace
4, run the trial test or full test
5, Go to tag: Result. High light the test you just did
6, Double click client-subtest or server-subtest. .pcap file should be there.
1, select the project you wanna do
2, Locate the tag: Run -> Config
3, enable client and server trace
4, run the trial test or full test
5, Go to tag: Result. High light the test you just did
6, Double click client-subtest or server-subtest. .pcap file should be there.
Thursday, July 17, 2008
Tuesday, July 8, 2008
Configure for FreeRadiusd
#more /etc/raddb/users
clilogin Auth-Type :=LOCAL, User-Password == "qa654321"
Service-Type = Framed-User,
Framed-Protocol = PPP,
Framed-IP-Address = 8.8.130.0,
Framed-IP-Netmask = 255.255.255.0,
Framed-Routing = Broadcast-Listen,
Framed-Filter-Id = "std.ppp",
Framed-MTU = 1500,
Framed-Compression = Van-Jacobsen-TCP-IP
sslvpnuser Auth-Type :=LOCAL, User-Password == "qa654321"
Service-Type = Framed-User,
Framed-Protocol = PPP,
Framed-IP-Address = 172.18.9.0,
Framed-IP-Netmask = 255.255.255.0,
Framed-Routing = Broadcast-Listen,
Framed-Filter-Id = "std.ppp",
Framed-MTU = 1500,
Framed-Compression = Van-Jacobsen-TCP-IP
msuser Auth-Type:= MS-CHAP, User-Password=="qa654321", Simultaneous-Use:=1
Service-Type = Framed-User,
Framed-Protocol = PPP,
Framed-IP-Address = 172.18.9.0,
Framed-IP-Netmask = 255.255.255.0,
Framed-Routing = Broadcast-Listen,
Framed-Filter-Id = "std.ppp",
Framed-MTU = 1500,
Framed-Compression = Van-Jacobsen-TCP-IP
chapuser Auth-Type:= CHAP, User-Password=="qa654321", Simultaneous-Use:=1
Service-Type = Framed-User,
Framed-Protocol = PPP,
Framed-IP-Address = 172.18.9.0,
Framed-IP-Netmask = 255.255.255.0,
Framed-Routing = Broadcast-Listen,
Framed-Filter-Id = "std.ppp",
Framed-MTU = 1500,
Framed-Compression = Van-Jacobsen-TCP-IP
#more client.conf
client 172.18.9.0/24 {
secret = test1
shortname = company-network
}
client 172.18.4.0/24 {
secret = test1
shortname = company-network
}
client 8.8.110.0/24 {
secret = test1
shortname = company-network
}
client 8.8.130.0/24 {
secret = test1
shortname = company-network
}
client 172.16.0.0/12 {
secret = test1
shortname = company-network
}
==== For new version from FC6 autoinstall ====
steve Cleartext-Password := "testing"
Service-Type = Framed-User,
Framed-Protocol = PPP,
Framed-IP-Address = 172.18.9.0,
Framed-IP-Netmask = 255.255.255.0,
Framed-Routing = Broadcast-Listen,
Framed-Filter-Id = "std.ppp",
Framed-MTU = 1500,
Framed-Compression = Van-Jacobsen-TCP-IP
[[[
# As of 1.1.4, you SHOULD NOT use Auth-Type. See "man rlm_pap"
# for a much better way of dealing with differing passwords.
]]]
====
(root) # d test authserver radius r169 chap steve testing
authenticate 'steve' against 'chap' succeeded, server=primary assigned_rad_session_id=21168128 session_timeout=0 secs!
(root) # exit
login: steve
Password: *******
Welcome !
3305 #
#more /etc/raddb/users
clilogin Auth-Type :=LOCAL, User-Password == "qa654321"
Service-Type = Framed-User,
Framed-Protocol = PPP,
Framed-IP-Address = 8.8.130.0,
Framed-IP-Netmask = 255.255.255.0,
Framed-Routing = Broadcast-Listen,
Framed-Filter-Id = "std.ppp",
Framed-MTU = 1500,
Framed-Compression = Van-Jacobsen-TCP-IP
sslvpnuser Auth-Type :=LOCAL, User-Password == "qa654321"
Service-Type = Framed-User,
Framed-Protocol = PPP,
Framed-IP-Address = 172.18.9.0,
Framed-IP-Netmask = 255.255.255.0,
Framed-Routing = Broadcast-Listen,
Framed-Filter-Id = "std.ppp",
Framed-MTU = 1500,
Framed-Compression = Van-Jacobsen-TCP-IP
msuser Auth-Type:= MS-CHAP, User-Password=="qa654321", Simultaneous-Use:=1
Service-Type = Framed-User,
Framed-Protocol = PPP,
Framed-IP-Address = 172.18.9.0,
Framed-IP-Netmask = 255.255.255.0,
Framed-Routing = Broadcast-Listen,
Framed-Filter-Id = "std.ppp",
Framed-MTU = 1500,
Framed-Compression = Van-Jacobsen-TCP-IP
chapuser Auth-Type:= CHAP, User-Password=="qa654321", Simultaneous-Use:=1
Service-Type = Framed-User,
Framed-Protocol = PPP,
Framed-IP-Address = 172.18.9.0,
Framed-IP-Netmask = 255.255.255.0,
Framed-Routing = Broadcast-Listen,
Framed-Filter-Id = "std.ppp",
Framed-MTU = 1500,
Framed-Compression = Van-Jacobsen-TCP-IP
#more client.conf
client 172.18.9.0/24 {
secret = test1
shortname = company-network
}
client 172.18.4.0/24 {
secret = test1
shortname = company-network
}
client 8.8.110.0/24 {
secret = test1
shortname = company-network
}
client 8.8.130.0/24 {
secret = test1
shortname = company-network
}
client 172.16.0.0/12 {
secret = test1
shortname = company-network
}
==== For new version from FC6 autoinstall ====
steve Cleartext-Password := "testing"
Service-Type = Framed-User,
Framed-Protocol = PPP,
Framed-IP-Address = 172.18.9.0,
Framed-IP-Netmask = 255.255.255.0,
Framed-Routing = Broadcast-Listen,
Framed-Filter-Id = "std.ppp",
Framed-MTU = 1500,
Framed-Compression = Van-Jacobsen-TCP-IP
[[[
# As of 1.1.4, you SHOULD NOT use Auth-Type. See "man rlm_pap"
# for a much better way of dealing with differing passwords.
]]]
====
(root) # d test authserver radius r169 chap steve testing
authenticate 'steve' against 'chap' succeeded, server=primary assigned_rad_session_id=21168128 session_timeout=0 secs!
(root) # exit
login: steve
Password: *******
Welcome !
3305 #
Test Multicast on FortiOS
1, test tools: mint
download link
2, command:
sender:
#mint -s 239.0.0.1 -p 4321 -n 1 -b 100 ; #default, ttl=1. it will cause some issue
FOS will decrement the ttl by one.
receiver:
#mint -r 239.0.0.1 -p 4321 -d 5
Ready to recieve packets:
Received 323 packets..
Notes: need to change the default route to make it make sense.
mint: invalid option -- -
Usage: mint -[s|r] [OPTIONS] ADDR
OPTIONS:
-h This help.
-N Don't log to file.
-L Specify alternate path for log file.(Default is /var/tmp/mint.log)
-r Configures MINT to be a multicast receiver.
-p specifies the port number MINT should listen to.
Default is 4321.
-d delay in seconds for waiting in receiving state.
Default is 1 second.
-s Configures MINT to be a multicast sender (Default).
-l specifies whether loopback should be enabled(1) or disable(0).
Disabled by default.
-p specifies the port MINT should send data to.
Default is 4321.
-t specifies the TTL MINT should use.
Default is 1.
-q specifies IP TOS.
IP Precedence Values are 0-7, default is 0
-n number of packets to be sent per second,
-1(default) means sends as many packets as possible.
DANGER: -1 creates a great deal of traffic.
-b specifies how much data to send in bytes.
-6 Using IPv6 instead of IPv4 (EXPERIMENTAL).
3, config on fortios:
config firewall multicast-policy
edit 1
set dstaddr 239.0.0.0 255.255.255.0
next
end
4, sniffer on FortiOS;
DS_127 (kontron) # d sniffer pack any udp 4
interfaces=[any]
filters=[udp]
0.517596 kvlan103 in 8.8.103.109.4321 -> 239.0.0.1.4321: udp 400
0.517611 kvlan104 out 8.8.103.109.4321 -> 239.0.0.1.4321: udp 400
0.517615 fabric1 out 8.8.103.109.4321 -> 239.0.0.1.4321: udp 400
1.521307 kvlan103 in 8.8.103.109.4321 -> 239.0.0.1.4321: udp 400
1.521318 kvlan104 out 8.8.103.109.4321 -> 239.0.0.1.4321: udp 400
1.521321 fabric1 out 8.8.103.109.4321 -> 239.0.0.1.4321: udp 400
2.525144 kvlan103 in 8.8.103.109.4321 -> 239.0.0.1.4321: udp 400
2.525153 kvlan104 out 8.8.103.109.4321 -> 239.0.0.1.4321: udp 400
5, IGMP report
http://nemesis.sourceforge.net/manpages/nemesis-igmp.1.html
1, test tools: mint
download link
2, command:
sender:
#mint -s 239.0.0.1 -p 4321 -n 1 -b 100 ; #default, ttl=1. it will cause some issue
FOS will decrement the ttl by one.
receiver:
#mint -r 239.0.0.1 -p 4321 -d 5
Ready to recieve packets:
Received 323 packets..
Notes: need to change the default route to make it make sense.
mint: invalid option -- -
Usage: mint -[s|r] [OPTIONS] ADDR
OPTIONS:
-h This help.
-N Don't log to file.
-L Specify alternate path for log file.(Default is /var/tmp/mint.log)
-r Configures MINT to be a multicast receiver.
-p specifies the port number MINT should listen to.
Default is 4321.
-d delay in seconds for waiting in receiving state.
Default is 1 second.
-s Configures MINT to be a multicast sender (Default).
-l specifies whether loopback should be enabled(1) or disable(0).
Disabled by default.
-p specifies the port MINT should send data to.
Default is 4321.
-t specifies the TTL MINT should use.
Default is 1.
-q specifies IP TOS.
IP Precedence Values are 0-7, default is 0
-n number of packets to be sent per second,
-1(default) means sends as many packets as possible.
DANGER: -1 creates a great deal of traffic.
-b specifies how much data to send in bytes.
-6 Using IPv6 instead of IPv4 (EXPERIMENTAL).
3, config on fortios:
config firewall multicast-policy
edit 1
set dstaddr 239.0.0.0 255.255.255.0
next
end
4, sniffer on FortiOS;
DS_127 (kontron) # d sniffer pack any udp 4
interfaces=[any]
filters=[udp]
0.517596 kvlan103 in 8.8.103.109.4321 -> 239.0.0.1.4321: udp 400
0.517611 kvlan104 out 8.8.103.109.4321 -> 239.0.0.1.4321: udp 400
0.517615 fabric1 out 8.8.103.109.4321 -> 239.0.0.1.4321: udp 400
1.521307 kvlan103 in 8.8.103.109.4321 -> 239.0.0.1.4321: udp 400
1.521318 kvlan104 out 8.8.103.109.4321 -> 239.0.0.1.4321: udp 400
1.521321 fabric1 out 8.8.103.109.4321 -> 239.0.0.1.4321: udp 400
2.525144 kvlan103 in 8.8.103.109.4321 -> 239.0.0.1.4321: udp 400
2.525153 kvlan104 out 8.8.103.109.4321 -> 239.0.0.1.4321: udp 400
5, IGMP report
http://nemesis.sourceforge.net/manpages/nemesis-igmp.1.html






